Page 173 - Photoreactive Organic Thin Films
P. 173
I 5 2 MIKHAIL V. KOZLOVSKY, LEV M. BLINOV, AND WOLFGANG HAASE
We should state that our suggested model is not completely justified yet,
but it remains the only one that can explain the whole ensemble of properties
observed for the isotropic smectic phase of P8*M and related polymers.
Keeping that in mind, we will refer hereafter to the mesophase as the IsoSm*
phase, which most probably has the ultrashort pitch TGB A* structure.
53 PHOTOINDUCED BIREFRINGENCE IN PHOTOCHROMIC ISOSM* COPOLYMERS
Because of the combination of short-scale smectic ordering, transparency,
and optical isotropy, the IsoSm* phase is promising for numerous optical and
photo-optical applications. We therefore prepared three series of copoly-
methacrylates combining the monomer matrix of P8*M with dichroic
comonomers based on different azobenzene dyes, namely /?-cyanoazobenzene
{SK series), p-mehoxyazobenzene (KW series), and /7-trifluoromethoxy-
73 74
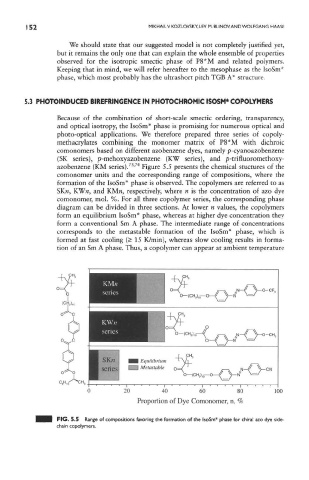
azobenzene (KM series). ' Figure 5.5 presents the chemical stuctures of the
comonomer units and the corresponding range of compositions, where the
formation of the IsoSm* phase is observed. The copolymers are referred to as
SK«, KWw, and KMn, respectively, where n is the concentration of azo dye
comonomer, mol. %. For all three copolymer series, the corresponding phase
diagram can be divided in three sections. At lower n values, the copolymers
form an equilibrium IsoSm* phase, whereas at higher dye concentration they
form a conventional Sm A phase. The intermediate range of concentrations
corresponds to the metastable formation of the IsoSm* phase, which is
formed at fast cooling (> 15 K/min), whereas slow cooling results in forma-
tion of an Sm A phase. Thus, a copolymer can appear at ambient temperature
FIG. 5.5 Range of compositions favoring the formation of the IsoSm* phase for chiral azo dye side-
chain copolymers.