Page 288 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 288
‘STRONG’ AND ‘WEAK’ ACIDS AND BASES 255
dilute aqueous solution of VII directly onto a post-operative wound
and found that the phenol killed all the bacteria, thereby yielding Phenol is a rare exam-
ple of a stable enol
the first reliable antiseptic in an era when medical science was in
its infancy. (pronounced ‘ene-ol’),
with a hydroxyl bonded
to a C=Cbond. Most
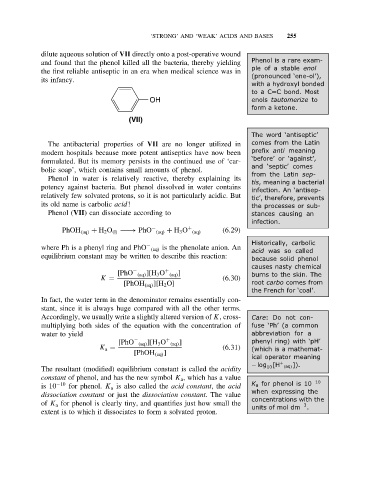
OH enols tautomerize to
form a ketone.
(VII)
The word ‘antiseptic’
The antibacterial properties of VII are no longer utilized in comes from the Latin
modern hospitals because more potent antiseptics have now been prefix anti meaning
‘before’ or ‘against’,
formulated. But its memory persists in the continued use of ‘car-
bolic soap’, which contains small amounts of phenol. and ‘septic’ comes
from the Latin sep-
Phenol in water is relatively reactive, thereby explaining its
tis, meaning a bacterial
potency against bacteria. But phenol dissolved in water contains
infection. An ‘antisep-
relatively few solvated protons, so it is not particularly acidic. But tic’, therefore, prevents
its old name is carbolic acid! the processes or sub-
Phenol (VII) can dissociate according to stances causing an
infection.
− +
PhOH (aq) + H 2 O (l) −−→ PhO (aq) + H 3 O (aq) (6.29)
Historically, carbolic
−
where Ph is a phenyl ring and PhO (aq) is the phenolate anion. An
acid was so called
equilibrium constant may be written to describe this reaction: because solid phenol
causes nasty chemical
+
−
[PhO (aq) ][H 3 O (aq) ] burns to the skin. The
K = (6.30)
[PhOH (aq) ][H 2 O] root carbo comes from
the French for ‘coal’.
In fact, the water term in the denominator remains essentially con-
stant, since it is always huge compared with all the other terms.
Accordingly, we usually write a slightly altered version of K, cross- Care:Do not con-
multiplying both sides of the equation with the concentration of fuse ‘Ph’ (a common
water to yield abbreviation for a
[PhO (aq) ][H 3 O (aq) ] phenyl ring) with ‘pH’
−
+
K a = (6.31) (which is a mathemat-
[PhOH (aq) ]
ical operator meaning
− log [H (aq) ]).
+
The resultant (modified) equilibrium constant is called the acidity 10
constant of phenol, and has the new symbol K a , which has a value −10
is 10 −10 for phenol. K a is also called the acid constant,the acid K a for phenol is 10
dissociation constant or just the dissociation constant. The value when expressing the
concentrations with the
of K a for phenol is clearly tiny, and quantifies just how small the −3
units of mol dm .
extent is to which it dissociates to form a solvated proton.