Page 357 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 357
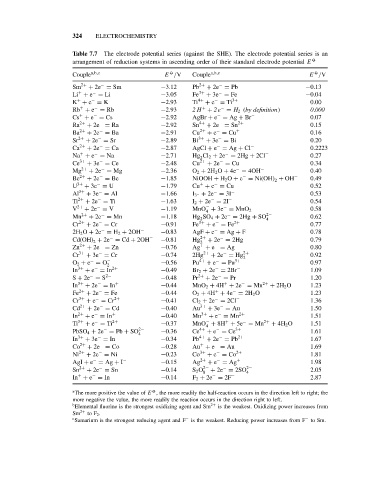
324 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
Table 7.7 The electrode potential series (against the SHE). The electrode potential series is an
arrangement of reduction systems in ascending order of their standard electrode potential E O
O
O
Couple a,b,c E /V Couple a,b,c E /V
−
−
Sm 2+ + 2e = Sm −3.12 Pb 2+ + 2e = Pb −0.13
Li + e = Li −3.05 Fe 3+ + 3e = Fe −0.04
+
−
−
+
−
−
K + e = K −2.93 Ti 4+ + e = Ti 3+ 0.00
+
+
−
Rb + e = Rb −2.93 2H + 2e = H 2 (by definition) 0.000
−
+
−
−
Cs + e = Cs −2.92 AgBr + e = Ag + Br − 0.07
Ra 2+ + 2e = Ra −2.92 Sn 4+ + 2e = Sn 2+ 0.15
−
−
−
−
Ba 2+ + 2e = Ba −2.91 Cu 2+ + e = Cu + 0.16
−
Sr 2+ + 2e = Sr −2.89 Bi 3+ + 3e = Bi 0.20
−
Ca 2+ + 2e = Ca −2.87 AgCl + e = Ag + Cl − 0.2223
−
−
−
+
−
Na + e = Na −2.71 Hg Cl 2 + 2e = 2Hg + 2Cl − 0.27
2
−
−
Ce 3+ + 3e = Ce −2.48 Cu 2+ + 2e = Cu 0.34
Mg 2+ + 2e = Mg −2.36 O 2 + 2H 2 O + 4e = 4OH − 0.40
−
−
−
Be 2+ + 2e = Be −1.85 NiOOH + H 2 O + e = Ni(OH) 2 + OH − 0.49
−
U 3+ + 3e = U −1.79 Cu + e = Cu 0.52
−
+
−
−
−
Al 3+ + 3e = Al −1.66 I 3 − + 2e = 3I − 0.53
−
Ti 2+ + 2e = Ti −1.63 I 2 + 2e = 2I − 0.54
−
−
V 2+ + 2e = V −1.19 − − 0.58
MnO + 3e = MnO 2
4
Mn 2+ + 2e = Mn −1.18 Hg SO 4 + 2e = 2Hg + SO 2− 0.62
−
−
2
4
−
Cr 2+ + 2e = Cr −0.91 Fe 3+ + e = Fe 2+ 0.77
−
−
2H 2 O + 2e = H 2 + 2OH − −0.83 AgF + e = Ag + F 0.78
−
Cd(OH) 2 + 2e = Cd + 2OH − −0.81 Hg 2+ + 2e = 2Hg 0.79
−
−
2
−
+
−
Zn 2+ + 2e = Zn −0.76 Ag + e = Ag 0.80
−
−
Cr 3+ + 3e = Cr −0.74 2Hg 2+ + 2e = Hg 2+ 0.92
2
O 2 + e = O − −0.56 Pu 4+ + e = Pu 3+ 0.97
−
−
2
−
In 3+ + e = In 2+ −0.49 Br 2 + 2e = 2Br − 1.09
−
−
−
S + 2e = S 2− −0.48 Pr 2+ + 2e = Pr 1.20
+
−
−
In 3+ + 2e = In + −0.44 MnO 2 + 4H + 2e = Mn 2+ + 2H 2 O 1.23
−
+
−
Fe 2+ + 2e = Fe −0.44 O 2 + 4H + 4e = 2H 2 O 1.23
−
Cr 3+ + e = Cr 2+ −0.41 Cl 2 + 2e = 2Cl − 1.36
−
−
Cd 2+ + 2e = Cd −0.40 Au 3+ + 3e = Au 1.50
−
−
−
In 2+ + e = In + −0.40 Mn 3+ + e = Mn 2+ 1.51
−
Ti 3+ + e = Ti 2+ −0.37 MnO + 8H + 5e = Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O 1.51
−
+
−
4
−
PbSO 4 + 2e = Pb + SO 2− −0.36 Ce 4+ + e = Ce 3+ 1.61
−
4
−
−
In 3+ + 3e = In −0.34 Pb 4+ + 2e = Pb 2+ 1.67
Co 2+ + 2e = Co −0.28 Au + e = Au 1.69
−
+
−
−
−
Ni 2+ + 2e = Ni −0.23 Co 3+ + e = Co 2+ 1.81
AgI + e = Ag + I − −0.15 Ag 2+ + e = Ag + 1.98
−
−
−
−
Sn 2+ + 2e = Sn −0.14 S 2 O 2− + 2e = 2SO 2− 2.05
8 4
+
In + e = In −0.14 F 2 + 2e = 2F − 2.87
−
−
a O
The more positive the value of E , the more readily the half-reaction occurs in the direction left to right; the
more negative the value, the more readily the reaction occurs in the direction right to left.
b 2+
Elemental fluorine is the strongest oxidizing agent and Sm is the weakest. Oxidizing power increases from
Sm 2+ to F 2 .
c Samarium is the strongest reducing agent and F is the weakest. Reducing power increases from F to Sm.
−
−