Page 362 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 362
HALF-CELLS AND THE NERNST EQUATION 329
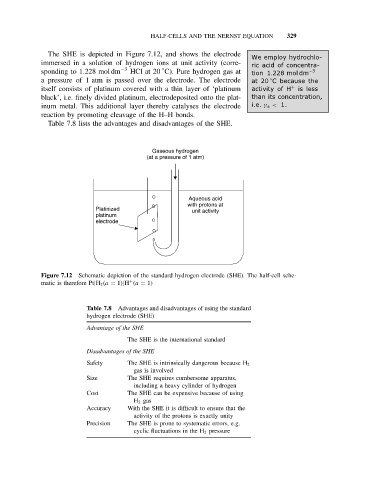
The SHE is depicted in Figure 7.12, and shows the electrode
We employ hydrochlo-
immersed in a solution of hydrogen ions at unit activity (corre- ric acid of concentra-
◦
sponding to 1.228 mol dm −3 HClat20 C). Pure hydrogen gas at tion 1.228 mol dm −3
a pressure of 1 atm is passed over the electrode. The electrode at 20 Cbecause the
◦
itself consists of platinum covered with a thin layer of ‘platinum activity of H + is less
black’, i.e. finely divided platinum, electrodeposited onto the plat- than its concentration,
inum metal. This additional layer thereby catalyses the electrode i.e. γ ± < 1.
reaction by promoting cleavage of the H–H bonds.
Table 7.8 lists the advantages and disadvantages of the SHE.
Gaseous hydrogen
(at a pressure of 1 atm)
Aqueous acid
with protons at
Platinized unit activity
platinum
electrode
Figure 7.12 Schematic depiction of the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). The half-cell sche-
+
matic is therefore Pt|H 2 (a = 1)|H (a = 1)
Table 7.8 Advantages and disadvantages of using the standard
hydrogen electrode (SHE)
Advantage of the SHE
The SHE is the international standard
Disadvantages of the SHE
Safety The SHE is intrinsically dangerous because H 2
gas is involved
Size The SHE requires cumbersome apparatus,
including a heavy cylinder of hydrogen
Cost The SHE can be expensive because of using
H 2 gas
Accuracy With the SHE it is difficult to ensure that the
activity of the protons is exactly unity
Precision The SHE is prone to systematic errors, e.g.
cyclic fluctuations in the H 2 pressure