Page 319 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 319
14/296Absolute Risk Estimates
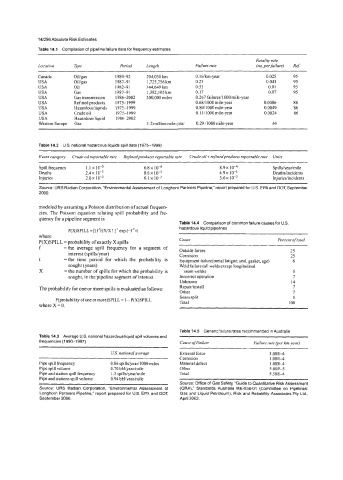
Table 14.1 Compilation of pipeline failure data for frequency estimates
Fatality rate
Location Trpe Period Length Failure rate (no. perfailure) Re$
Canada Oiligas 1989-92 294,030 km 0.16h-year 0.025 95
USA Oiligas 1987-91 1,725,156 km 0.25 0.043 95
USA Oil 1982-91 344,649 km 0.55 0.01 95
USA Gas 1987-9 1 1,382,105 !an 0.17 0.07 95
USA Gas transmission 1986-2002 300,000 miles 0.267 failures/lOOO mile-year
USA Refined products 1975-1999 0.6811000 mile-year 0.0086 86
USA Hazardous liquids 1975-1999 0.8911000 mile-year 0.0049 86
USA Crude oil 1975-1999 0.1 1ilOOOmile-year 0.0024 86
USA Hazardous liquid 1986-2002
Western Europe Gas 1.2 million mile-year 0.29 /lo00 mile-year 44
Table 14.2 U.S. national hazardous liquids spill data (1975-1999)
Event category Crude oil reportable rate Refinedproducts reportable rate Crude oil + refinedproducts reportable rate Units
Spill frequency 1.1 x 10-3 6.8 x IO4 8.9~ Spillsiyearimile
IO"
Deaths 2.4 x 10-3 8.6 x lo-' 4.9 x 10-3 Deathsiincidents
Injuries 2.0 x 10-2 6.1 x 3.6~ Injuriesiincidents
Source: URS Radian Corporation, "Environmental Assessment of Lonqhorn Partners Pipeline," report prepared for U.S. EPA and DOT, September
2000.
modeled by assuming a Poisson distribution of actual frequen-
cies. The Poisson equation relating spill probability and fie-
quency for a pipeline segment is
Table 14.4 Comparison of common failure causes for U.S.
P(X)SPILL = [(f *t)X/X ! ] * exp (-f * t) hazardous liquid pipelines
where ~~
P(X)SPILL =probability of exactly X spills Cause Percent of total
f =the average spill frequency for a segment of
interest (spills/year) Outside forces 25
25
Corrosion
t =the time period for which the probability is Equipment failure(meta1 fatigue, seal, gasket, age) 6
sought (years) Weld failure (all welds except longitudinal
X =the number of spills for which the probability is seam welds) 5
sought, in the pipeline segment of interest. Incorrect operation 7
Unknown 14
The probability for one or more spills is evaluated as follows: Repairiinstall 7
Other I
Seam split 5
P(prohahi1ity nfone 0rmore)SPILL = 1 - P(X)SPILL
where X = 0. Total 100
Tabla 14.5 Generic failure rates recommended in Australia
Table 14.3 Average US. national hazardous liquid spill volumes and
frequencies (1990-1997) Cause ofFailure Failure rate per h-year)
US. national average External force 3.00E-4
Corrosion 1 .DOE4
Pipe spill frequency 0.86 spillsiyearl1000 miles Material defect 1.00E-4
Pipe spill volume 0.70 hhl/year/mile Other 5.OOE-5
Pipe and station spill frequency 1.3 spillsiyearlmile Total 5.50E4
Pipe and stations spill volume 0.94 bhllyearimile
Source: Office of Gas Safety, "Guide to Quantitative Risk Assessment
Source: URS Radian Corporation, "Environmental Assessment of (ORA)," Standards Australia ME-038-01 (Committee on Pipelines:
Longhorn Partners Pipeline." report prepared for U.S. EPA and DOT, Gas and Liquid Petroleum), Risk and Reliability Associates Pty Ltd..
September 2000. April 2002.