Page 74 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 74
Assessing third-party damage potential 3/53
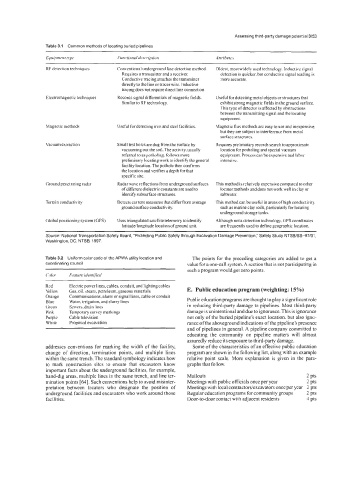
Table 3.1 Common methods of locating buried pipelines
Equipment hpe Functional description Attributes
RF detection techniques Conventional underground line detection method. Oldest, most widely used technology. Inductive signal
Requires a transmitter and a receiver. detection is quicker. but conductive signal reading is
Conductive tracing attaches the transmitter more accurate.
directly to the line or tracer wire. Inductive
tracing does not require direct line connection.
Electromagnetic techniques Records signal differentials of magnetic fields. Useful for detecting metal objects or structures that
Similar to RF technology. exhibit strong magnetic fields in the ground surface.
This type of detector is affected hy obstructions
between the transmitting signal and the locating
equipment.
Magnetic method< Useful for detecting iron and steel facilities. Magnetic flux methods are easy to use and inexpensive.
but they are subject to interference from metal
surface structures.
Vacuum extraction Small test holes are dug from the surface by Requires preliminary records search to approximate
vacuuming out the soil. The activity, usually location for potholing and special vacuum
referred to aspotholing, follows more equipment. Process can be expensive and labor
preliminary locating work to identify the general intensive.
facility location. The pothole then confirms
the location and verifies a depth for that
specific site.
Ground penetrating radar Radar wave reflections from underground surfaces This method is relatively expensive compared to other
of different dielectric constants are used to locator methods and does not work well in clay or
identify subsurface structures. saltwater.
Terrain conductivity Detects current measures that differ from average This method can be useful in areas of high conductivity,
ground surface conductivity. such as marine clay soils, particularly for locating
underground storage tanks.
Global positioning system (GPS) Uses triangulated satellite telemetry to identify Although not a detection technology. GPS coordinates
latitude/longitude location ofground unit. are frequently used to define geographic location.
Source: National Transportation Safety Board, "Protecting Public Safety through Excavation Damage Prevention," Safety Study NTSB/SS-97/01,
Washington, DC: NTSB, 1997.
Table 3.2 Uniform color code of the APWA utility location and The points for the preceding categories are added to get a
coordinating council value for a one-call system. A section that is not participating in
such a program would get zero points.
Color. Feuture identified
Red Electric power lines, cables, conduit, and lighting cables
Yellow Gas, oil, steam, petroleum, gaseous materials E. Public education program (weighting: 15%)
Orange Communications, alarm or signal lines, cable or conduit
Blue Water, irrigation. and slurry lines Public education programs are thought to play a significant role
Green Sewers, drain lines in reducing third-party damage to pipelines. Most third-party
Pink Temporary survey markings damage is unintentional and due to ignorance. This is ignorance
Purple Cable television not only of the buried pipeline's exact location, but also igno-
White Proposed excavation rance of the aboveground indications of the pipeline's presence
and of pipelines in general. A pipeline company committed to
educating the community on pipeline matters will almost
assuredly reduce its exposure to third-party damage.
addresses conventions for marking the width of the facility, Some of the characteristics of an effective public education
change of direction, termination points, and multiple lines program are shown in the following list, along with an example
within the same trench. The standard symbology indicates how relative point scale. More explanation is given in the para-
to mark construction sites to ensure that excavators know graphs that follow.
important facts about the underground facilities, for example,
hand-dig areas, multiple lines in the same trench, and line ter- Mailouts 2 pts
mination points [64]. Such conventions help to avoid misinter- Meetings with public officials once per year 2 pts
pretation between locators who designate the position of Meetings with local contractors/excavators once per year 2 pts
underground facilities and excavators who work around those Regular education programs for community groups 2 pts
facilities. Door-to-door contact with adjacent residents 4 pts