Page 261 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 261
Polyaniline-based nanocomposites for hydrogen storage 233
store only lower than 1 wt% at room temperature and about 100 bar. However, the
storage capacity could be considerably increased at cryogenic temperature [54].H 2
sorption capacity for purified SWCNTs was observed to be of 2.4 wt% at 77 K
[55]. Furthermore, acid treatment of the SWCNTs demonstrates that the hydrogen
sorption capacity is increased from 1 to 1.7 wt% at 77 K and 1 bar [52].
Stefanakos et al. prepared a nanocomposite with PANI and multiwalled carbon
nanotubes (MWCNTs). PANI-based nanocomposites were altered by adding 10%
of filler material, that is, MWCNTs, so as to improve the porous formation and to
increase the number of adsorbing sites in the nanocomposite to achieve the efficient
hydrogen uptake capacity. Addition of filler material to the PANI matrix enhances the
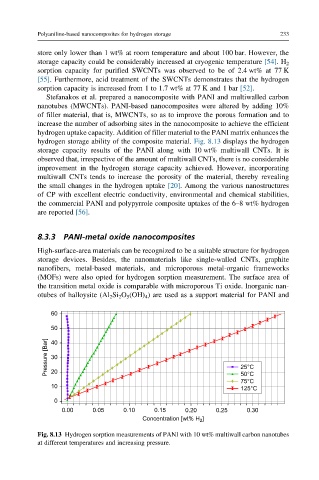
hydrogen storage ability of the composite material. Fig. 8.13 displays the hydrogen
storage capacity results of the PANI along with 10 wt% multiwall CNTs. It is
observed that, irrespective of the amount of multiwall CNTs, there is no considerable
improvement in the hydrogen storage capacity achieved. However, incorporating
multiwall CNTs tends to increase the porosity of the material, thereby revealing
the small changes in the hydrogen uptake [20]. Among the various nanostructures
of CP with excellent electric conductivity, environmental and chemical stabilities,
the commercial PANI and polypyrrole composite uptakes of the 6–8 wt% hydrogen
are reported [56].
8.3.3 PANI-metal oxide nanocomposites
High-surface-area materials can be recognized to be a suitable structure for hydrogen
storage devices. Besides, the nanomaterials like single-walled CNTs, graphite
nanofibers, metal-based materials, and microporous metal-organic frameworks
(MOFs) were also opted for hydrogen sorption measurement. The surface area of
the transition metal oxide is comparable with microporous Ti oxide. Inorganic nan-
otubes of halloysite (Al 2 Si 2 O 5 (OH) 4 ) are used as a support material for PANI and
60
50
Pressure [Bar] 30 25°C
40
20
50°C
75°C
10 125°C
0
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30
Concentration [wt% H ]
2
Fig. 8.13 Hydrogen sorption measurements of PANI with 10 wt% multiwall carbon nanotubes
at different temperatures and increasing pressure.