Page 128 - Power Electronic Control in Electrical Systems
P. 128
//SYS21/F:/PEC/REVISES_10-11-01/075065126-CH004.3D ± 116 ± [106±152/47] 17.11.2001 9:54AM
116 Power flows in compensation and control studies
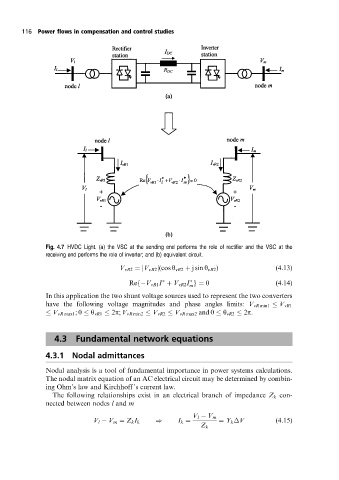
Fig. 4.7 HVDC Light. (a) the VSC at the sending end performs the role of rectifier and the VSC at the
receiving end performs the role of inverter; and (b) equivalent circuit.
V vR2 jV vR2 j(cos y vR2 j sin y vR2 ) (4:13)
Ref V vR1 I V vR2 I g 0 (4:14)
m
In this application the two shunt voltage sources used to represent the two converters
have the following voltage magnitudes and phase angles limits: V vR min1 V vR1
V vR max1 ;0 y vR1 2p; V vR min2 V vR2 V vR max2 and 0 y vR2 2p.
4.3 Fundamental network equations
4.3.1 Nodal admittances
Nodal analysis is a tool of fundamental importance in power systems calculations.
The nodal matrix equation of an AC electrical circuit may be determined by combin-
ing Ohm's law and Kirchhoff 's current law.
The following relationships exist in an electrical branch of impedance Z k con-
nected between nodes l and m
V l V m
V l V m Z k I k ) I k Y k V (4:15)
Z k