Page 221 - Power Electronic Control in Electrical Systems
P. 221
//SYS21/F:/PEC/REVISES_10-11-01/075065126-CH006.3D ± 209 ± [177±262/86] 17.11.2001 10:23AM
Power electronic control in electrical systems 209
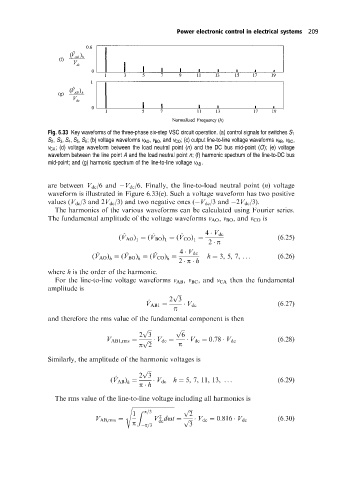
Fig. 6.33 Key waveforms of the three-phase six-step VSC circuit operation. (a) control signals for switches S 1
S 2 ¸ S 3 ¸ S 4 ¸ S 5 ¸ S 6 ; (b) voltage waveforms v AO ¸ v BO ¸ and v CO ; (c) output line-to-line voltage waveforms v AB ¸ v BC ¸
v CA ; (d) voltage waveform between the load neutral point (n) and the DC bus mid-point (O); (e) voltage
waveform between the line point A and the load neutral point n; (f) harmonic spectrum of the line-to-DC bus
mid-point; and (g) harmonic spectrum of the line-to-line voltage v AB .
are between V dc /6 and V dc /6. Finally, the line-to-load neutral point (n) voltage
waveform is illustrated in Figure 6.33(e). Such a voltage waveform has two positive
values (V dc /3 and 2V dc /3) and two negative ones ( V dc /3 and 2V dc /3).
The harmonics of the various waveforms can be calculated using Fourier series.
The fundamental amplitude of the voltage waveforms v AO , v BO ,and v CO is
^ ^ ^ 4 V dc
(V AO ) (V BO ) (V CO ) 2 p (6:25)
1
1
1
^ ^ ^ 4 V dc
(V AO ) (V BO ) (V CO ) h 3, 5, 7, ... (6:26)
h
h
h
2 p h
where h is the order of the harmonic.
For the line-to-line voltage waveforms v AB , v BC , and v CA then the fundamental
amplitude is
p
2 3
^
V AB1 V dc (6:27)
p
and therefore the rms value of the fundamental component is then
p p
2 3 6
V AB1,rms p V dc V dc 0:78 V dc (6:28)
p 2 p
Similarly, the amplitude of the harmonic voltages is
p
2 3
^
(V AB ) V dc h 5, 7, 11, 13, ... (6:29)
h
p h
The rms value of the line-to-line voltage including all harmonics is
s p
p=3
1 Z 2
2
V AB,rms V dot p V dc 0:816 V dc (6:30)
dc
p p=3 3