Page 87 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 87
80 Power semiconductor control components
temperature variation in V,, given by equation (3.1), and so enables this
circuit to maintain much greater frequency stability than conventional UJT
systems.
3.3.3 The diac
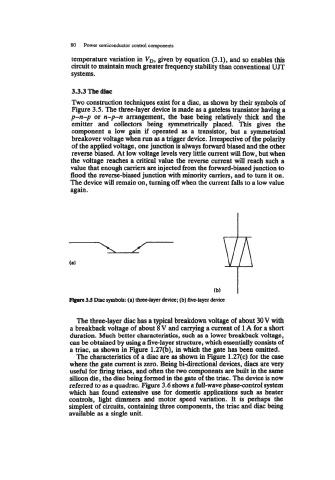
Two construction techniques exist for a diac, as shown by their symbols of
Figure 3.5. The three-layer device is made as a gateless transistor having a
p-n-p or n-p-n arrangement, the base being relatively thick and the
emitter and collectors being symmetrically placed. This gives the
component a low gain if operated as a transistor, but a symmetrical
breakover voltage when run as a trigger device. Irrespective of the polarity
of the applied voltage, one junction is always forward biased and the other
reverse biased. At low voltage levels very little current will flow, but when
the voltage reaches a critical value the reverse current will reach such a
value that enough carriers are injected from the forward-biased junction to
flood the reverse-biased junction with minority carriers, and to turn it on.
The device will remain on, turning off when the current falls to a low value
again.
(b) I
3.5 Diac symboh (a) three-layer device; (b) five-layer device
The three-layer diac has a typical breakdown voltage of about 30 V with
a breakback voltage of about 8 V and canying a current of 1 A for a short
duration. Much better characteristics, such as a lower breakback voltage,
can be obtained by using a five-layer structure, which essentially consists of
a triac, as shown in Figure 1.27(b), in which the gate has been omitted.
The characteristics of a diac are as shown in Figure 1.27(c) for the case
where the gate current is zero. Being bidirectional devices, diacs are very
useful for firing triacs, and often the two components are built in the same
silicon die, the diac being formed in the gate of the triac. The device is now
referred to as a quadrac. Figure 3.6 shows a full-wave phase-control system
which has found extensive use for domestic applications such as heater
controls, light dimmers and motor speed variation. It is perhaps the
simplest of circuits, containing three components, the triac and diac being
available as a single unit.