Page 198 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 198
180 Chapter Twelve
Voltage disturbances
Three types of voltage disturbances affect ASDs: voltage sags, voltage
interruptions, and voltage unbalance. In textile and paper mills, a brief
voltage sag may potentially cause an ASD to introduce speed fluctuations
that can damage the end product at severe cost. Furthermore, a brief
voltage sag can also cause a momentary decrease in dc-link voltage,
triggering an under-voltage trip or resulting in an over-current trip of
the ASD [12.8].
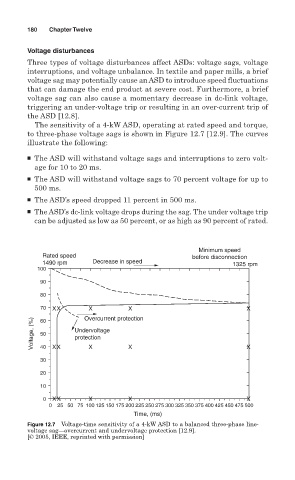
The sensitivity of a 4-kW ASD, operating at rated speed and torque,
to three-phase voltage sags is shown in Figure 12.7 [12.9]. The curves
illustrate the following:
■ The ASD will withstand voltage sags and interruptions to zero volt-
age for 10 to 20 ms.
■ The ASD will withstand voltage sags to 70 percent voltage for up to
500 ms.
■ The ASD’s speed dropped 11 percent in 500 ms.
■ The ASD’s dc-link voltage drops during the sag. The under voltage trip
can be adjusted as low as 50 percent, or as high as 90 percent of rated.
Minimum speed
Rated speed before disconnection
1490 rpm Decrease in speed 1325 rpm
100
90
80
X
70 X X Overcurrent protection X
X
Voltage, (%) 60 Undervoltage
50
protection
40
30 X X X X X
20
10
0 X X X X X
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
Time, (ms)
Figure 12.7 Voltage-time sensitivity of a 4-kW ASD to a balanced three-phase line-
voltage sag—overcurrent and undervoltage protection [12.9].
[© 2005, IEEE, reprinted with permission]