Page 37 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 37
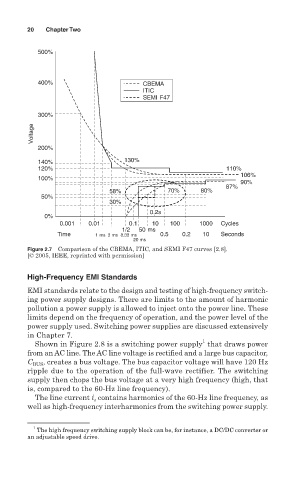
20 Chapter Two
500%
400% CBEMA
ITIC
SEMI F47
300%
Voltage
200%
140% 130%
120% 110%
106%
100%
90%
87%
58% 70% 80%
50%
30%
0.2s
0%
0.001 0.01 0.1 10 100 1000 Cycles
1/2 50 ms
Time 1 ms 3 ms 8.33 ms 0.5 0.2 10 Seconds
20 ms
Figure 2.7 Comparison of the CBEMA, ITIC, and SEMI F47 curves [2.8].
[© 2005, IEEE, reprinted with permission]
High-Frequency EMI Standards
EMI standards relate to the design and testing of high-frequency switch-
ing power supply designs. There are limits to the amount of harmonic
pollution a power supply is allowed to inject onto the power line. These
limits depend on the frequency of operation, and the power level of the
power supply used. Switching power supplies are discussed extensively
in Chapter 7.
1
Shown in Figure 2.8 is a switching power supply that draws power
from an AC line. The AC line voltage is rectified and a large bus capacitor,
C BUS , creates a bus voltage. The bus capacitor voltage will have 120 Hz
ripple due to the operation of the full-wave rectifier. The switching
supply then chops the bus voltage at a very high frequency (high, that
is, compared to the 60-Hz line frequency).
contains harmonics of the 60-Hz line frequency, as
The line current i s
well as high-frequency interharmonics from the switching power supply.
1
The high frequency switching supply block can be, for instance, a DC/DC converter or
an adjustable speed drive.