Page 114 - Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
P. 114
112 Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
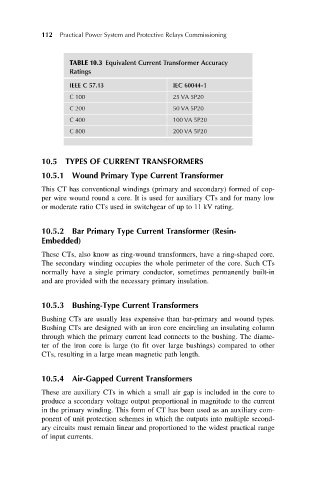
TABLE 10.3 Equivalent Current Transformer Accuracy
Ratings
IEEE C 57.13 IEC 60044-1
C 100 25 VA 5P20
C 200 50 VA 5P20
C 400 100 VA 5P20
C 800 200 VA 5P20
10.5 TYPES OF CURRENT TRANSFORMERS
10.5.1 Wound Primary Type Current Transformer
This CT has conventional windings (primary and secondary) formed of cop-
per wire wound round a core. It is used for auxiliary CTs and for many low
or moderate ratio CTs used in switchgear of up to 11 kV rating.
10.5.2 Bar Primary Type Current Transformer (Resin-
Embedded)
These CTs, also know as ring-wound transformers, have a ring-shaped core.
The secondary winding occupies the whole perimeter of the core. Such CTs
normally have a single primary conductor, sometimes permanently built-in
and are provided with the necessary primary insulation.
10.5.3 Bushing-Type Current Transformers
Bushing CTs are usually less expensive than bar-primary and wound types.
Bushing CTs are designed with an iron core encircling an insulating column
through which the primary current lead connects to the bushing. The diame-
ter of the iron core is large (to fit over large bushings) compared to other
CTs, resulting in a large mean magnetic path length.
10.5.4 Air-Gapped Current Transformers
These are auxiliary CTs in which a small air gap is included in the core to
produce a secondary voltage output proportional in magnitude to the current
in the primary winding. This form of CT has been used as an auxiliary com-
ponent of unit protection schemes in which the outputs into multiple second-
ary circuits must remain linear and proportioned to the widest practical range
of input currents.