Page 100 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 100
90 code, Gray COHERENCE
do not lead to significant errors when the adjacent digital val- and the Frank code and offset some of the problems inherent
ues intersect. SAL in the Frank codes and step FM. SAL
Ref.: Sloka (1970), p. 141; Jordan (1985), p. 43.5. Ref.: Barton (1991), pp. 7.20–7.23; Lewis (1986), pp. 10–12.
e 1
A perfect code is a code having a sidelobe structure contain-
8
ing the minimum energy theoretically possible, with this
e
t 3 energy uniformly distributed among the sidelobes. The
0
Barker code is an example. SAL
Input A
-+ - - - + + 16
+
- + - - - + + + Ref.: Morris (1988), p. 135.
Summer
e 1 Output phase coding (see MODULATION, phase).
+
e e
Summer 2 3 t polarization coding (see MODULATION, polarization).
+ - + + - + + + 0
+ + + -+ + + e 2 A polyphase code is a sequence of symbols with more than
-
Input B
8 two discrete values, used to form polyphase coded wave-
forms. Instead of only two phase shift values, 0 and 180 deg
,
t
0 as in the binary phase code, smaller increments can be
applied. A quadriphase code is a polyphase code with four
Figure C33 Matched-filter response to Golay code. phase values: 0, 90, 180, and 270° This code can be gener-
.
ated from a binary phase code using conversion formula
(
sk 1– )
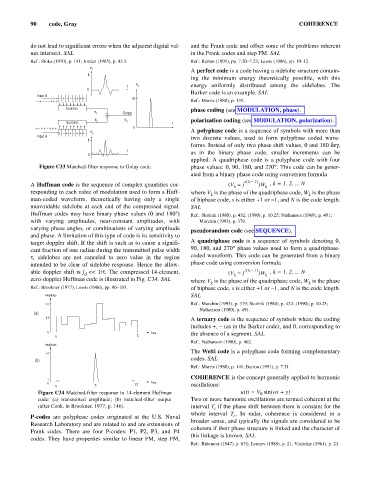
A Huffman code is the sequence of complex quantities cor- ( V = j ) W k , k = 1, 2, ... N
k
responding to each value of modulation used to form a Huff- where V is the phase of the quadriphase code, W is the phase
k
k
man-coded waveform, theoretically having only a single of biphase code, s is either +1 or -1, and N is the code length.
unavoidable sidelobe at each end of the compressed signal. SAL
Huffman codes may have binary phase values (0 and 180°) Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 432, (1990), p. 10.25; Nathanson (1969), p. 491;
with varying amplitudes, near-constant amplitudes, with Morchin (1993), p. 379.
varying phase angles, or combinations of varying amplitude
pseudorandom code (see SEQUENCE).
and phase. A limitation of this type of code is its sensitivity to
target doppler shift. If the shift is such as to cause a signifi- A quadriphase code is a sequence of symbols denoting 0,
cant fraction of one radian during the transmitted pulse width 90, 180, and 270° phase values used to form a quadriphase-
t sidelobes are not canceled to zero value in the region coded waveform. This code can be generated from a binary
,
intended to be clear of sidelobe response. Hence the allow- phase code using conversion formula
(
able doppler shift is f << 1/t. The compressed 14-element, ( V = j sk 1– ) ) W k , k = 1, 2, ... N
d
k
zero-doppler Huffman code is illustrated in Fig. C34. SAL where V is the phase of the quadriphase code, W is the phase
k
k
Ref.: Brookner (1977); Lewis (1986), pp. 96–105. of biphase code, s is either +1 or -1, and N is the code length.
Amplitude SAL
1.0 Ref.: Morchin (1993), p. 379; Skolnik (1980), p. 432; (1990), p. 10.25;
Nathanson (1980), p. 491.
(a)
A ternary code is the sequence of symbols where the coding
0.5
includes +, - (as in the Barker code), and 0, corresponding to
0 Time the absence of a segment. SAL
0 t
Ref.: Nathanson (1990), p. 462.
Amplitude
The Welti code is a polyphase code forming complementary
14
codes. SAL
(b)
Ref.: Morris (1988), p. 141; Barton (1991), p. 7.31.
COHERENCE is the concept generally applied to harmonic
1
0 t 2t Time oscillations:
0
Figure C34 Matched-filter response to 14-element Huffman u(t) = V sin(wt + y)
0
code: (a) transmitted amplitude; (b) matched-filter output Two or more harmonic oscillations are termed coherent at the
(after Cook, in Brookner, 1977, p. 146). interval T if the phase shift between them is constant for the
c
whole interval T . In radar, coherence is considered in a
c
P-codes are polyphase codes originated at the U.S. Naval
broader sense, and typically the signals are considered to be
Research Laboratory and are related to and are extensions of
coherent if their phase structure is linked and the character of
Frank codes. There are four P-codes: P1, P2, P3, and P4
this linkage is known. SAL
codes. They have properties similar to linear FM, step FM,
Ref.: Ridenour (1947), p. 631; Leonov (1988), p. 21; Vinitskiy (1961), p. 23.