Page 132 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 132
122 detection probability detection, reliability of
two probabilities can be calculated, for a given threshold, if
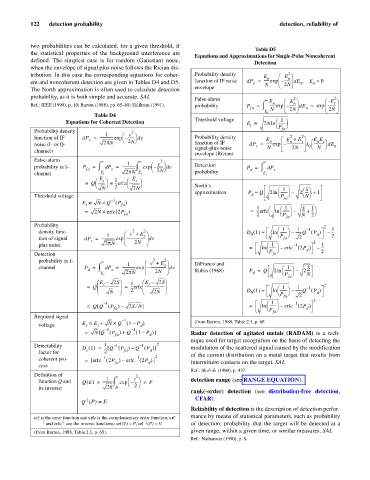
Table D5
the statistical properties of the background interference are
Equations and Approximations for Single-Pulse Noncoherent
defined. The simplest case is for random (Gaussian) noise, Detection
when the envelope of signal plus noise follows the Rician dis-
2
tribution. In this case the corresponding equations for coher- Probability density E n æ E ö
n
ent and noncoherent detection are given in Tables D4 and D5. function of IF noise dP = ------ exp è – ç ------- ÷ dE E >, n 0
e
n
2N
N
ø
The North approximation is often used to calculate detection envelope
probability, as it is both simple and accurate. SAL False-alarm ¥ 2 2
E ö
E ö
n
t
Ref.: IEEE (1990), p. 10; Barton (1988), pp. 65–68; Skillman (1991). probability P = ò E n æ – ç ------- ÷ dE = exp ç – æ --------- ÷
------ exp
fa N 2N n 2N
E t è ø è ø
Table D4
Threshold voltage 1
Equations for Coherent Detection E = 2Nln æ ------- ö
t è P ø
Probability density 2 fa
1 æ v ö
function of IF dP = --------------- exp – ------- dv Probability density 2 2
v è 2N ø E n E + E s E E
æ
n
n s ö
noise (I- or Q- 2p N function of IF dP = ------ exp – ------------------ I ------------ dE
s
0 è
signal-plus-noise N 2N N ø n
channel)
envelope (Rician)
False-alarm ¥ ¥ 2 ¥
1
v ö
probability in I- P = ò d P = --------------- ò exp æ – ------- d v Detection P = d P
fa v è 2N ø d ò s
channel E t 2pN E t probability E t
E E
æ t ö 1 æ t ö
= Q -------- = ---erfc -----------
è ø 2 è ø North’s
N 2N 1 S
ö
æö
approximation P » Q 2ln æ ------- – 2 ---- + 1
N
Threshold voltage d è P fa ø èø
– 1
E = N ´ Q ( P )
t fa
1 æ æ 1 ö S 1 ö
= 2N ´ erfc 2P ) = ---erfc ln ------- – ---- + ---
(
fa 2 è è P ø N 2 ø
fa
Probability 2
1
1
1
–
ö
density func- 2 2 D 1 ()» ln æ ------- – -------Q ( P ) – 1 ---
1 æ v + E ö 0 è P ø d 2
s
tion of signal dP = --------------- exp – ç ----------------- ÷ dv fa 2
s 2N 2
plus noise 2pN è ø æ 1 ö – 1 1
= ln ------- – erfc ( 2P ) – ---
è P ø d 2
Detection fa
probability in I- ¥ æ v + E ö DiFranco and
2
2
1
s
channel P = ò d P = ---------------exp – ç ----------------- ÷ dv 1 S
ö
d s 2N Rubin (1968) P = Q 2ln æ ------- – 2----
E t 2pN è ø d è P ø N
fa
æ E – 2S ö 1 æ E – 2S ö
t
t
= Q --------------------- ÷ ---erfc --------------------- ÷ æ 1 ö 1 – 1 2
=
ç
ç
è N ø 2 è 2N ø D 1 () » ln è ------- – -------Q ( P )
0
d
ø
P
fa 2
2
– 1 æ 1 ö – 1
¤
= QQ ([ P ) 2SN ] = ln ------- – erfc ( 2P )
–
fa è P ø d
fa
Required signal
– 1 (from Barton, 1988, Table 2.3, p. 68.
voltage E = E + N ´ Q ( 1 – P )
d
s
t
– 1 – 1
+
[
= NQ ( P ) Q ( 1 – P )]
fa d Radar detection of agitated metals (RADAM) is a tech-
nique used for target recognition on the basis of detecting the
Detectability 1 – 1 – 1 2
–
=
D 1 () --- Q ([ P fa ) Q ( P )] modulation of the scattered signal caused by the modification
d
c
factor for 2 of the current distribution on a metal target that results from
2
–
–
1
1
coherent pro- = [ erfc ( 2P fa ) erfc ( 2P )]
–
d
cess intermittent contacts on the target. SAL
Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 437.
Definition of ¥ 2
1 v ö
function Q and QE = ò exp æ – ----- = P detection range (see RANGE EQUATION).
() ----------
è
its inverse: 2p E 2 ø
rank(-order) detection (see distribution-free detection,
-1
Q (P) = E CFAR).
Reliability of detection is the description of detection perfor-
erf is the error function and erfc is the complementary error function; erf - mance by means of statistical parameters, such as probability
1 -1 - 1
and erfc are the inverse functions: erf(V) = P, erf (P) = V. of detection: probability that the target will be detected at a
(from Barton, 1988, Table 2.1, p. 65). given range, within a given time, or similar measures. SAL
Ref.: Nathanson (1990), p. 8.