Page 68 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 68
58 attenuation by snow attenuator, calibration
(a)
(b)
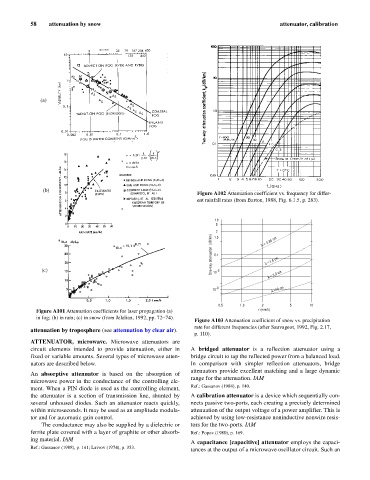
Figure A102 Attenuation coefficient vs. frequency for differ-
ent rainfall rates (from Barton, 1988, Fig. 6.1.5, p. 283).
10
5
2 0.86 cm
One-way attenuation (dB/km) 0.1 l = l = 1.8 cm
1.0
(c) 10 -2
l = 3.2 cm
10 -3 l = 10 cm
0.5 1.0 2 5 10
Figure A101 Attenuation coefficients for laser propagation (a) r (mm/h)
in fog; (b) in rain; (c) in snow (from Jelalian, 1992, pp. 72–74).
Figure A103 Attenuation coefficient of snow vs. precipitation
rate for different frequencies (after Sauvageot, 1992, Fig. 2.17,
attenuation by troposphere (see attenuation by clear air).
p. 110).
ATTENUATOR, microwave. Microwave attenuators are
circuit elements intended to provide attenuation, either in A bridged attenuator is a reflection attenuator using a
fixed or variable amounts. Several types of microwave atten- bridge circuit to tap the reflected power from a balanced load.
uators are described below. In comparison with simpler reflection attenuators, bridge
attenuators provide excellent matching and a large dynamic
An absorptive attenuator is based on the absorption of
range for the attenuation. IAM
microwave power in the conductance of the controlling ele-
ment. When a PIN diode is used as the controlling element, Ref.: Gassanov (1988), p. 140.
the attenuator is a section of transmission line, shunted by A calibration attenuator is a device which sequentially con-
several unhoused diodes. Such an attenuator reacts quickly, nects passive two-ports, each creating a precisely determined
within microseconds. It may be used as an amplitude modula- attenuation of the output voltage of a power amplifier. This is
tor and for automatic gain control. achieved by using low-resistance noninductive nonwire resis-
The conductance may also be supplied by a dielectric or tors for the two-ports. IAM
ferrite plate covered with a layer of graphite or other absorb- Ref.: Popov (1980), p. 169.
ing material. IAM
A capacitance [capacitive] attenuator employs the capaci-
Ref.: Gassanov (1988), p. 141; Lavrov (1974), p. 353.
tances at the output of a microwave oscillator circuit. Such an