Page 63 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 63
4.2 The Continuous Associative Completion 49
a) b) c) d)
x 3
x 3
x 3
x 2
x 2
s 2
x 1 x 2
x 1
s 1
S
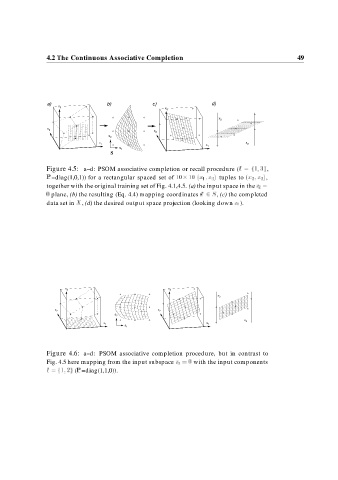
Figure 4.5: a–d: PSOM associative completion or recall procedure (I f g,
P=diag(1,0,1)) for a rectangular spaced set of x x tuples to x , x
together with the original training set of Fig. 4.1,4.5. (a) the input space in the x
plane, (b) the resulting (Eq. 4.4) mapping coordinates s S, (c) the completed
data set in X, (d) the desired output space projection (looking down x ).
x 3 x 3
x 3
x 2 x 2
s 2
x 2
x 1 x 1
s 1
Figure 4.6: a–d: PSOM associative completion procedure, but in contrast to
Fig. 4.5 here mapping from the input subspace x with the input components
I f
g (P=diag(1,1,0)).