Page 152 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 152
10 Diode Recti®ers 141
voltage waveforms v D1 and v D2 in Fig. 10.4, it is clear that the
peak inverse voltage (PIV) of the diodes is equal to 2V during
m
their blocking state. Hence the Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage
(V RRM ) rating of the diodes must be chosen to be higher than
2V to avoid reverse breakdown. (Note that, compared with
m
the half-wave recti®er shown in Fig. 10.1, the full-wave
recti®er has twice the dc output voltage, as shown in Section
10.2.4.) During its conducting state, each diode has a forward
current that is equal to the load current and, therefore, the
Peak Repetitive Forward Current (I ) rating of these diodes
FRM
must be chosen to be higher than the peak load current V =R
m
in practice.
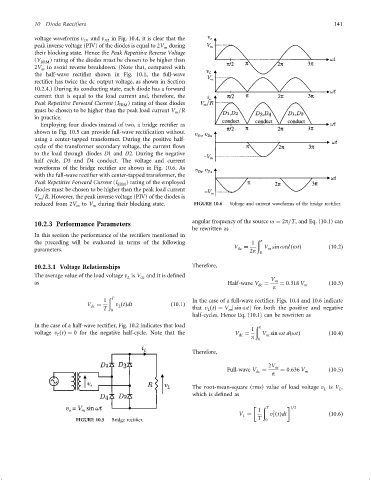
Employing four diodes instead of two, a bridge recti®er as
shown in Fig. 10.5 can provide full-wave recti®cation without
using a center-tapped transformer. During the positive half-
cycle of the transformer secondary voltage, the current ¯ows
to the load through diodes D1 and D2. During the negative
half cycle, D3 and D4 conduct. The voltage and current
waveforms of the bridge recti®er are shown in Fig. 10.6. As
with the full-wave recti®er with center-tapped transformer, the
Peak Repetitive Forward Current (I FRM ) rating of the employed
diodes must be chosen to be higher than the peak load current
V =R. However, the peak inverse voltage (PIV) of the diodes is
m
reduced from 2V to V during their blocking state. FIGURE 10.6 Voltage and current waveforms of the bridge recti®er.
m
m
10.2.3 Performance Parameters angular frequency of the source o ¼ 2p=T, and Eq. (10.1) can
be rewritten as
In this section the performance of the recti®ers mentioned in
the preceding will be evaluated in terms of the following 1 ð p
V ¼ V sin otd ðotÞ ð10:2Þ
parameters. dc 2p 0 m
10.2.3.1 Voltage Relationships Therefore,
The average value of the load voltage v is V and it is de®ned V
L
dc
as Half-wave V ¼ m ¼ 0:318 V m ð10:3Þ
dc
p
ð T
1 In the case of a full-wave recti®er, Figs. 10.4 and 10.6 indicate
V ¼ v ðtÞdt ð10:1Þ
dc
L
T 0 that v ðtÞ¼ V j sin otj for both the positive and negative
L
m
half-cycles. Hence Eq. (10.1) can be rewritten as
In the case of a half-wave recti®er, Fig. 10.2 indicates that load ð p
1
voltage v ðtÞ¼ 0 for the negative half-cycle. Note that the V ¼ V sin otdðotÞ ð10:4Þ
L
dc
m
p 0
Therefore,
2V m
Full-wave V ¼ ¼ 0:636 V ð10:5Þ
dc p m
The root-mean-square (rms) value of load voltage v is V ,
L L
which is de®ned as
ð T 1=2
1 2
V ¼ v ðtÞdt ð10:6Þ
L
L
FIGURE 10.5 Bridge recti®er. T 0