Page 156 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 156
Design of Residential Photovoltaic Systems 143
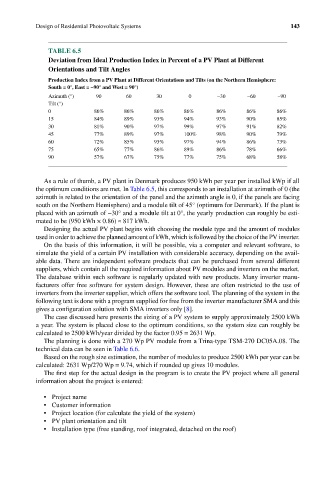
TABLE 6.5
Deviation from Ideal Production Index in Percent of a PV Plant at Different
Orientations and Tilt Angles
Production Index from a PV Plant at Different Orientations and Tilts (on the Northern Hemisphere:
South = 0°, East = −90° and West = 90°)
Azimuth (°) 90 60 30 0 −30 −60 −90
Tilt (°)
0 86% 86% 86% 86% 86% 86% 86%
15 84% 89% 93% 94% 93% 90% 85%
30 81% 90% 97% 99% 97% 91% 82%
45 77% 89% 97% 100% 98% 90% 79%
60 72% 85% 93% 97% 94% 86% 73%
75 65% 77% 86% 89% 86% 78% 66%
90 57% 67% 75% 77% 75% 68% 58%
As a rule of thumb, a PV plant in Denmark produces 950 kWh per year per installed kWp if all
the optimum conditions are met. In Table 6.5, this corresponds to an installation at azimuth of 0 (the
azimuth is related to the orientation of the panel and the azimuth angle is 0, if the panels are facing
south on the Northern Hemisphere) and a module tilt of 45° (optimum for Denmark). If the plant is
placed with an azimuth of −30° and a module tilt at 0°, the yearly production can roughly be esti-
mated to be (950 kWh × 0.86) ≈ 817 kWh.
Designing the actual PV plant begins with choosing the module type and the amount of modules
used in order to achieve the planned amount of kWh, which is followed by the choice of the PV inverter.
On the basis of this information, it will be possible, via a computer and relevant software, to
simulate the yield of a certain PV installation with considerable accuracy, depending on the avail-
able data. There are independent software products that can be purchased from several different
suppliers, which contain all the required information about PV modules and inverters on the market.
The database within such software is regularly updated with new products. Many inverter manu-
facturers offer free software for system design. However, these are often restricted to the use of
inverters from the inverter supplier, which offers the software tool. The planning of the system in the
following text is done with a program supplied for free from the inverter manufacturer SMA and this
gives a configuration solution with SMA inverters only [8].
The case discussed here presents the sizing of a PV system to supply approximately 2500 kWh
a year. The system is placed close to the optimum conditions, so the system size can roughly be
calculated to 2500 kWh/year divided by the factor 0.95 = 2631 Wp.
The planning is done with a 270 Wp PV module from a Trina-type TSM-270 DC05A.08. The
technical data can be seen in Table 6.6.
Based on the rough size estimation, the number of modules to produce 2500 kWh per year can be
calculated: 2631 Wp/270 Wp = 9.74, which if rounded up gives 10 modules.
The first step for the actual design in the program is to create the PV project where all general
information about the project is entered:
• Project name
• Customer information
• Project location (for calculate the yield of the system)
• PV plant orientation and tilt
• Installation type (free standing, roof integrated, detached on the roof)