Page 215 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 215
202 Renewable Energy Devices and Systems with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS ®
®
2500
IGBT
Diode
2000
Instantaneous power loss (W) 1500
1000
500
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Time (s)
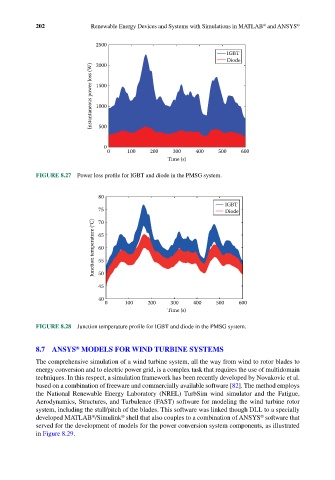
FIGURE 8.27 Power loss profile for IGBT and diode in the PMSG system.
80
IGBT
75 Diode
70
Junction temperature (°C) 65
60
55
50
45
40
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Time (s)
FIGURE 8.28 Junction temperature profile for IGBT and diode in the PMSG system.
8.7 ANSYS MODELS FOR WIND TURBINE SYSTEMS
®
The comprehensive simulation of a wind turbine system, all the way from wind to rotor blades to
energy conversion and to electric power grid, is a complex task that requires the use of multidomain
techniques. In this respect, a simulation framework has been recently developed by Novakovic et al.
based on a combination of freeware and commercially available software [82]. The method employs
the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) TurbSim wind simulator and the Fatigue,
Aerodynamics, Structures, and Turbulence (FAST) software for modeling the wind turbine rotor
system, including the stall/pitch of the blades. This software was linked though DLL to a specially
®
®
developed MATLAB /Simulink shell that also couples to a combination of ANSYS software that
®
served for the development of models for the power conversion system components, as illustrated
in Figure 8.29.