Page 84 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 84
Three-Phase Photovoltaic Systems: Structures, Topologies, and Control 71
4.3 THREE-PHASE PV INVERTER TOPOLOGIES
Three-phase PV inverters are the key elements in the transformation of the DC power from PV
arrays into a grid-synchronized AC power. In the case of single-phase systems, besides the classi-
cal half-bridge and H-bridge topologies, there are many different topologies proposed in different
publications during the last 10 years; some of these topologies are also used within the industry
today [23–27].
Nevertheless, in the case of three-phase systems, the variety of topologies is not so big. One can
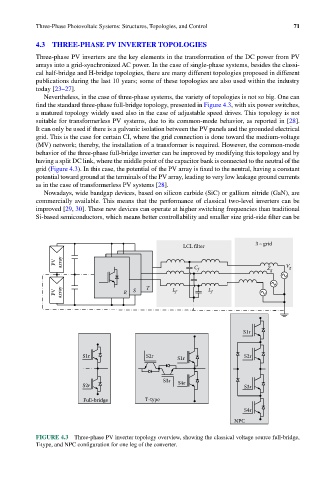
find the standard three-phase full-bridge topology, presented in Figure 4.3, with six power switches,
a matured topology widely used also in the case of adjustable speed drives. This topology is not
suitable for transformerless PV systems, due to its common-mode behavior, as reported in [28].
It can only be used if there is a galvanic isolation between the PV panels and the grounded electrical
grid. This is the case for certain CI, where the grid connection is done toward the medium-voltage
(MV) network; thereby, the installation of a transformer is required. However, the common-mode
behavior of the three-phase full-bridge inverter can be improved by modifying this topology and by
having a split DC link, where the middle point of the capacitor bank is connected to the neutral of the
grid (Figure 4.3). In this case, the potential of the PV array is fixed to the neutral, having a constant
potential toward ground at the terminals of the PV array, leading to very low leakage ground currents
as in the case of transformerless PV systems [28].
Nowadays, wide bandgap devices, based on silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN), are
commercially available. This means that the performance of classical two-level inverters can be
improved [29, 30]. These new devices can operate at higher switching frequencies than traditional
Si-based semiconductors, which means better controllability and smaller size grid-side filter can be
LCL filter 3~grid
PV array C f Z g V g
PV array R S T L f L f
S1r
S1r S2r S1r S2r
S3r S4r
S2r S3r
Full-bridge T-type
S4r
NPC
FIGURE 4.3 Three-phase PV inverter topology overview, showing the classical voltage source full-bridge,
T-type, and NPC configuration for one leg of the converter.