Page 91 -
P. 91
4.4 T tests 77
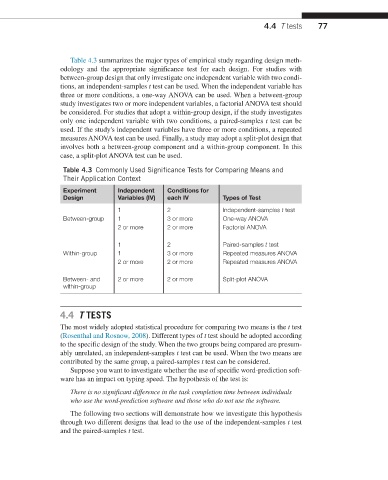
Table 4.3 summarizes the major types of empirical study regarding design meth-
odology and the appropriate significance test for each design. For studies with
between-group design that only investigate one independent variable with two condi-
tions, an independent-samples t test can be used. When the independent variable has
three or more conditions, a one-way ANOVA can be used. When a between-group
study investigates two or more independent variables, a factorial ANOVA test should
be considered. For studies that adopt a within-group design, if the study investigates
only one independent variable with two conditions, a paired-samples t test can be
used. If the study's independent variables have three or more conditions, a repeated
measures ANOVA test can be used. Finally, a study may adopt a split-plot design that
involves both a between-group component and a within-group component. In this
case, a split-plot ANOVA test can be used.
Table 4.3 Commonly Used Significance Tests for Comparing Means and
Their Application Context
Experiment Independent Conditions for
Design Variables (IV) each IV Types of Test
1 2 Independent-samples t test
Between-group 1 3 or more One-way ANOVA
2 or more 2 or more Factorial ANOVA
1 2 Paired-samples t test
Within-group 1 3 or more Repeated measures ANOVA
2 or more 2 or more Repeated measures ANOVA
Between- and 2 or more 2 or more Split-plot ANOVA
within-group
4.4 T TESTS
The most widely adopted statistical procedure for comparing two means is the t test
(Rosenthal and Rosnow, 2008). Different types of t test should be adopted according
to the specific design of the study. When the two groups being compared are presum-
ably unrelated, an independent-samples t test can be used. When the two means are
contributed by the same group, a paired-samples t test can be considered.
Suppose you want to investigate whether the use of specific word-prediction soft-
ware has an impact on typing speed. The hypothesis of the test is:
There is no significant difference in the task completion time between individuals
who use the word-prediction software and those who do not use the software.
The following two sections will demonstrate how we investigate this hypothesis
through two different designs that lead to the use of the independent-samples t test
and the paired-samples t test.