Page 241 - Robot Builder's Bonanza
P. 241
210 MOVING YOUR ROBOT
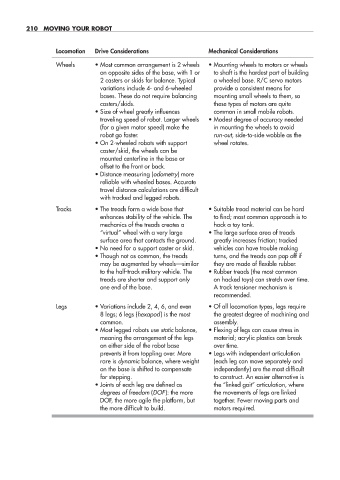
Locomotion Drive Considerations Mechanical Considerations
Wheels • Most common arrangement is 2 wheels • Mounting wheels to motors or wheels
on opposite sides of the base, with 1 or to shaft is the hardest part of building
2 casters or skids for balance. Typical a wheeled base. R/C servo motors
variations include 4- and 6- wheeled provide a consistent means for
bases. These do not require balancing mounting small wheels to them, so
casters/skids. these types of motors are quite
• Size of wheel greatly influences common in small mobile robots.
traveling speed of robot. Larger wheels • Modest degree of accuracy needed
(for a given motor speed) make the in mounting the wheels to avoid
robot go faster. run- out, side- to- side wobble as the
• On 2- wheeled robots with support wheel rotates.
caster/skid, the wheels can be
mounted centerline in the base or
offset to the front or back.
• Distance measuring (odometry) more
reliable with wheeled bases. Accurate
travel distance calculations are difficult
with tracked and legged robots.
Tracks • The treads form a wide base that • Suitable tread material can be hard
enhances stability of the vehicle. The to find; most common approach is to
mechanics of the treads creates a hack a toy tank.
“virtual” wheel with a very large • The large surface area of treads
surface area that contacts the ground. greatly increases friction; tracked
• No need for a support caster or skid. vehicles can have trouble making
• Though not as common, the treads turns, and the treads can pop off if
may be augmented by wheels— similar they are made of flexible rubber.
to the half- track military vehicle. The • Rubber treads (the most common
treads are shorter and support only on hacked toys) can stretch over time.
one end of the base. A track tensioner mechanism is
recommended.
Legs • Variations include 2, 4, 6, and even • Of all locomotion types, legs require
8 legs; 6 legs (hexapod) is the most the greatest degree of machining and
common. assembly.
• Most legged robots use static balance, • Flexing of legs can cause stress in
meaning the arrangement of the legs material; acrylic plastics can break
on either side of the robot base over time.
prevents it from toppling over. More • Legs with independent articulation
rare is dynamic balance, where weight (each leg can move separately and
on the base is shifted to compensate independently) are the most difficult
for stepping. to construct. An easier alternative is
• Joints of each leg are defined as the “linked gait” articulation, where
degrees of freedom (DOF): the more the movements of legs are linked
DOF, the more agile the platform, but together. Fewer moving parts and
the more difficult to build. motors required.
20-chapter-20.indd 210 4/21/11 11:50 AM