Page 87 - Robotics Designing the Mechanisms for Automated Machinery
P. 87
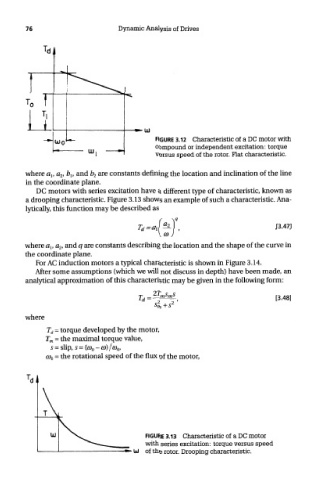
76 Dynamic Analysis of Drives
FIGURE 3.12 Characteristic of a DC motor with
compound or independent excitation: torque
versus speed of the rotor. Flat characteristic.
where a lt a 2, b lt and b 2 are constants defining the location and inclination of the line
in the coordinate plane.
DC motors with series excitation have a different type of characteristic, known as
a drooping characteristic. Figure 3.13 shows an example of such a characteristic. Ana-
lytically, this function may be described as
where a lt a 2, and q are constants describing the location and the shape of the curve in
the coordinate plane.
For AC induction motors a typical characteristic is shown in Figure 3.14.
After some assumptions (which we will not discuss in depth) have been made, an
analytical approximation of this characteristic may be given in the following form:
where
T d - torque developed by the motor,
T m = the maximal torque value,
s = slip, s=(a> 0-tD)/6) 0,
(0 Q = the rotational speed of the flux of the motor,
FIGURE 3.13 Characteristic of a DC motor
with series excitation: torque versus speed
of the rotor. Drooping characteristic.