Page 144 - Science at the nanoscale
P. 144
8:11
RPS: PSP0007 - Science-at-Nanoscale
June 9, 2009
Low-Dimensional Nanostructures
134
facets of the growing nanocrystals. Such tunability of the shape
and band-gap is very attractive for applications in nanocrystal-
based solar cells.
Quantum wires
6.3.2
Surface melting assisted oxidisation can be used to directly grow
metal oxide nanostructures without the presence of solution or
vapour. Here, we shall detail the commonly used vapour based
method and introduce a simple and straightforward thermal
heating technique for the growth of 1D nanowires.
The vapour-based route is a widely adopted approach for the
fabrication of metal oxide nanostructures.
vapour can be achieved in many ways including simple thermal
evaporation, laser ablation, sputtering, arc discharge, etc. Typical-
ly, the precursor vapour is transported by a gas flow from source
to the deposition substrate at a certain temperature range. The
process is often implemented in a furnace chamber, such as a tube
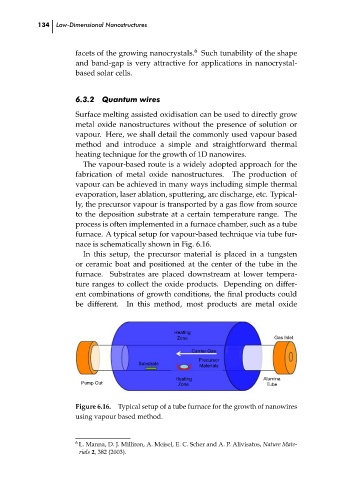
furnace. A typical setup for vapour-based technique via tube fur-
nace is schematically shown in Fig. 6.16.
In this setup, the precursor material is placed in a tungsten
or ceramic boat and positioned at the center of the tube in the
furnace. Substrates are placed downstream at lower tempera-
ture ranges to collect the oxide products. Depending on differ-
ent combinations of growth conditions, the final products could
be different.
In this method, most products are metal oxide
Heating 6 The production of ch06
Zone Gas Inlet
Carrier Gas
Precursor
Substrate
Materials
Heating Alumina
Pump Out Zone Tube
Figure 6.16. Typical setup of a tube furnace for the growth of nanowires
using vapour based method.
6 L. Manna, D. J. Milliron, A. Meisel, E. C. Scher and A. P. Alivisatos, Nature Mate-
rials 2, 382 (2003).