Page 145 - Sedimentology and Stratigraphy
P. 145
132 Rivers and Alluvial Fans
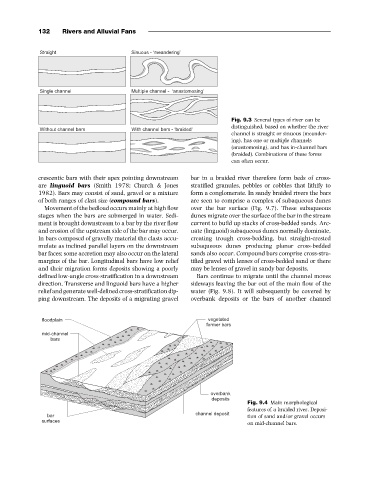
Fig. 9.3 Several types of river can be
distinguished, based on whether the river
channel is straight or sinuous (meander-
ing), has one or multiple channels
(anastomosing), and has in-channel bars
(braided). Combinations of these forms
can often occur.
crescentic bars with their apex pointing downstream bar in a braided river therefore form beds of cross-
are linguoid bars (Smith 1978; Church & Jones stratified granules, pebbles or cobbles that lithify to
1982). Bars may consist of sand, gravel or a mixture form a conglomerate. In sandy braided rivers the bars
of both ranges of clast size (compound bars). are seen to comprise a complex of subaqueous dunes
Movement of the bedload occurs mainly at high flow over the bar surface (Fig. 9.7). These subaqueous
stages when the bars are submerged in water. Sedi- dunes migrate over the surface of the bar in the stream
ment is brought downstream to a bar by the river flow current to build up stacks of cross-bedded sands. Arc-
and erosion of the upstream side of the bar may occur. uate (linguoid) subaqueous dunes normally dominate,
In bars composed of gravelly material the clasts accu- creating trough cross-bedding, but straight-crested
mulate as inclined parallel layers on the downstream subaqueous dunes producing planar cross-bedded
bar faces; some accretion may also occur on the lateral sands also occur. Compound bars comprise cross-stra-
margins of the bar. Longitudinal bars have low relief tified gravel with lenses of cross-bedded sand or there
and their migration forms deposits showing a poorly may be lenses of gravel in sandy bar deposits.
defined low-angle cross-stratification in a downstream Bars continue to migrate until the channel moves
direction. Transverse and linguoid bars have a higher sideways leaving the bar out of the main flow of the
relief and generate well-defined cross-stratification dip- water (Fig. 9.8). It will subsequently be covered by
ping downstream. The deposits of a migrating gravel overbank deposits or the bars of another channel
Fig. 9.4 Main morphological
features of a braided river. Deposi-
tion of sand and/or gravel occurs
on mid-channel bars.