Page 52 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 52
Elastic Properties: The Stressed Uniform Lattice
lombic (electrostatic) force between the net charges of the constituent
“ions” form the bond. This bond is sometimes termed localized,
because the electrons are tightly bound to the participating atoms.
• van der Waals—a very weak bonding force that is often termed the
fluctuating dipole force because it is proportional to an induced dipole
between the constituent atoms, and this effective dipole moment has a
non-vanishing time average.
• Valency—another localized electron-pair bond. Here, the electron-
pair of the participating atoms form a hybrid orbital that is equally
shared by the two atoms, hence the term covalent. Clearly, ionic and
covalent bonds are the two limiting cases of a similar phenomena, so
that a bond in-between these limits can also be expected. Valency
bonds are quite strong, and account for the hardness and brittle nature
of the materials.
• Metallic—the electrons participating in the bonding are non-local-
ized. Typically, the number of valence electrons at a point is exceeded
by the number of nearest-neighbor atoms. The electrons are therefore
shared by many atoms, making them much more mobile, and also
accounts for the ductility of the material.
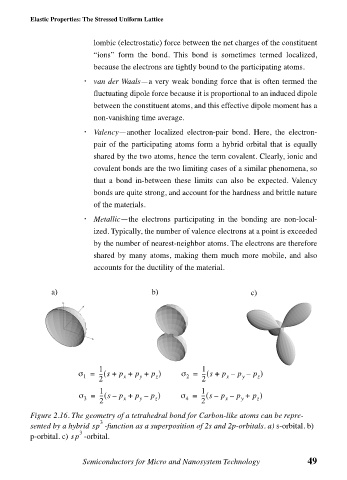
a) b) c)
1 1
σ = --- s +( p + p + p ) σ = --- s +( p – p – p )
1 x y z 2 x y z
2 2
1 1
σ = --- s –( p + p – p ) σ = --- s –( p – p + p )
3 x y z 4 x y z
2 2
Figure 2.16. The geometry of a tetrahedral bond for Carbon-like atoms can be repre-
3
sented by a hybrid sp -function as a superposition of 2s and 2p-orbitals. a) s-orbital. b)
3
p-orbital. c) sp -orbital.
Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology 49