Page 57 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 57
The Crystal Lattice System
For silicon, this model works well with the following parameters:
G = 7.0495563 , H = 0.60222456 , p = , 4 q = , 0 λ = 21 ,
γ = 1.2 , the cut-off radius c = 1.8 , the “lattice” constant
– 19
⁄
a = 0.20951nm and the bond energy E = 6.9447×10 J ion . Note
that in the above r = r – r .
ij i j
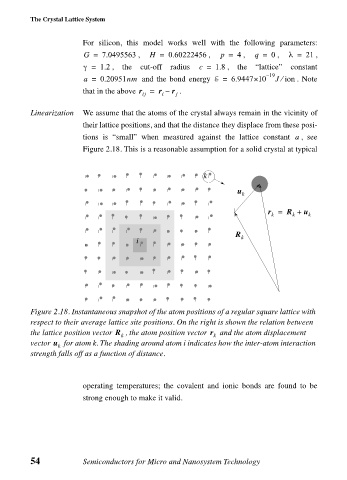
Linearization We assume that the atoms of the crystal always remain in the vicinity of
their lattice positions, and that the distance they displace from these posi-
tions is “small” when measured against the lattice constant a , see
Figure 2.18. This is a reasonable assumption for a solid crystal at typical
k
u
k
r = R + u
k k k
R k
i
Figure 2.18. Instantaneous snapshot of the atom positions of a regular square lattice with
respect to their average lattice site positions. On the right is shown the relation between
the lattice position vector R , the atom position vector r and the atom displacement
k k
vector u for atom k. The shading around atom i indicates how the inter-atom interaction
k
strength falls off as a function of distance.
operating temperatures; the covalent and ionic bonds are found to be
strong enough to make it valid.
54 Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology