Page 17 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 17
Geng(SMH)_CH02.qxd 04/04/2005 19:33 Page 2.4
IC DESIGN
2.4 SEMICONDUCTOR FUNDAMENTALS AND BASIC MATERIALS
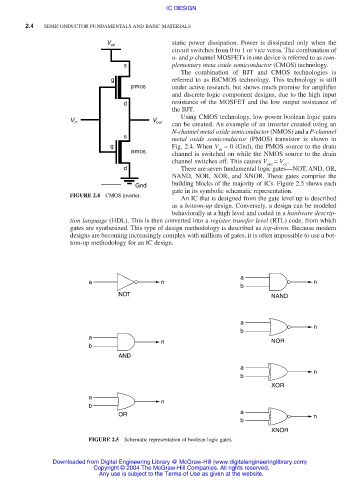
V cc static power dissipation. Power is dissipated only when the
circuit switches from 0 to 1 or vice versa. The combination of
n- and p-channel MOSFETs in one device is referred to as com-
s plementary meta oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology.
The combination of BJT and CMOS technologies is
g referred to as BiCMOS technology. This technology is still
pmos under active research, but shows much promise for amplifier
and discrete logic component designs, due to the high input
d resistance of the MOSFET and the low output resistance of
the BJT.
Using CMOS technology, low-power boolean logic gates
V in V out can be created. An example of an inverter created using an
N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) and a P-channel
s
metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor is shown in
g Fig. 2.4. When V = 0 (Gnd), the PMOS source to the drain
in
nmos channel is switched on while the NMOS source to the drain
channel switches off. This causes V = V .
out cc
d There are seven fundamental logic gates—NOT, AND, OR,
NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. These gates comprise the
Gnd building blocks of the majority of ICs. Figure 2.5 shows each
gate in its symbolic schematic representation.
FIGURE 2.4 CMOS inverter.
An IC that is designed from the gate level up is described
as a bottom-up design. Conversely, a design can be modeled
behaviorally at a high level and coded in a hardware descrip-
tion language (HDL). This is then converted into a register transfer level (RTL) code, from which
gates are synthesized. This type of design methodology is described as top-down. Because modern
designs are becoming increasingly complex with millions of gates, it is often impossible to use a bot-
tom-up methodology for an IC design.
a
a n n
b
NOT NAND
a
n
b
a
n NOR
b
AND
a
n
b
XOR
a
n
b
a
OR n
b
XNOR
FIGURE 2.5 Schematic representation of boolean logic gates.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.