Page 16 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 16
Geng(SMH)_CH02.qxd 04/04/2005 19:33 Page 2.3
IC DESIGN
IC DESIGN 2.3
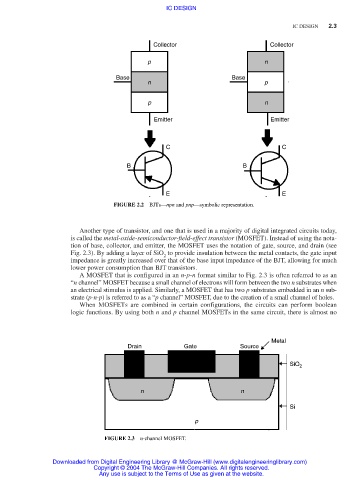
Collector Collector
p n
Base Base
n p
p n
Emitter Emitter
C C
B B
E E
FIGURE 2.2 BJTs—npn and pnp—symbolic representation.
Another type of transistor, and one that is used in a majority of digital integrated circuits today,
is called the metal-oxide-semiconductor-field-effect transistor (MOSFET). Instead of using the nota-
tion of base, collector, and emitter, the MOSFET uses the notation of gate, source, and drain (see
Fig. 2.3). By adding a layer of SiO to provide insulation between the metal contacts, the gate input
2
impedance is greatly increased over that of the base input impedance of the BJT, allowing for much
lower power consumption than BJT transistors.
A MOSFET that is configured in an n-p-n format similar to Fig. 2.3 is often referred to as an
“n channel” MOSFET because a small channel of electrons will form between the two n substrates when
an electrical stimulus is applied. Similarly, a MOSFET that has two p substrates embedded in an n sub-
strate (p-n-p) is referred to as a “p channel” MOSFET, due to the creation of a small channel of holes.
When MOSFETs are combined in certain configurations, the circuits can perform boolean
logic functions. By using both n and p channel MOSFETs in the same circuit, there is almost no
Metal
Drain Gate Source
SiO 2
n n
Si
p
FIGURE 2.3 n-channel MOSFET.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.