Page 226 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 226
bud29281_ch04_147-211.qxd 11/27/09 2:55PM Page 201 ntt 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
Deflection and Stiffness 201
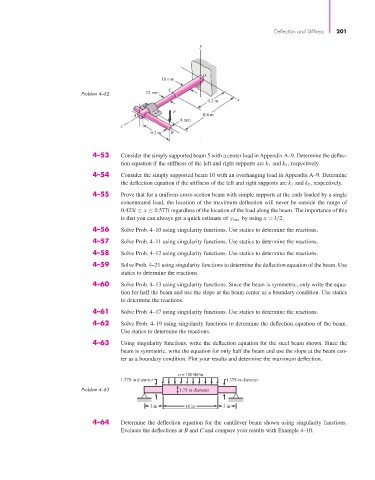
y
O
18 mm
C
Problem 4–52 12 mm
0.2 m x
F
A 0.4 m
8 mm
z
0.2 m B
4–53 Consider the simply supported beam 5 with a center load in Appendix A–9. Determine the deflec-
tion equation if the stiffness of the left and right supports are k 1 and k 2 , respectively.
4–54 Consider the simply supported beam 10 with an overhanging load in Appendix A–9. Determine
the deflection equation if the stiffness of the left and right supports are k 1 and k 2 , respectively.
4–55 Prove that for a uniform-cross-section beam with simple supports at the ends loaded by a single
concentrated load, the location of the maximum deflection will never be outside the range of
0.423l ≤ x ≤ 0.577l regardless of the location of the load along the beam. The importance of this
is that you can always get a quick estimate of y max by using x = l/2.
4–56 Solve Prob. 4–10 using singularity functions. Use statics to determine the reactions.
4–57 Solve Prob. 4–11 using singularity functions. Use statics to determine the reactions.
4–58 Solve Prob. 4–12 using singularity functions. Use statics to determine the reactions.
4–59 Solve Prob. 4–21 using singularity functions to determine the deflection equation of the beam. Use
statics to determine the reactions.
4–60 Solve Prob. 4–13 using singularity functions. Since the beam is symmetric, only write the equa-
tion for half the beam and use the slope at the beam center as a boundary condition. Use statics
to determine the reactions.
4–61 Solve Prob. 4–17 using singularity functions. Use statics to determine the reactions.
4–62 Solve Prob. 4–19 using singularity functions to determine the deflection equation of the beam.
Use statics to determine the reactions.
4–63 Using singularity functions, write the deflection equation for the steel beam shown. Since the
beam is symmetric, write the equation for only half the beam and use the slope at the beam cen-
ter as a boundary condition. Plot your results and determine the maximum deflection.
w = 180 lbf/in
1.375-in diameter 1.375-in diameter
Problem 4–63 1.75-in diameter
3 in 10 in 3 in
4–64 Determine the deflection equation for the cantilever beam shown using singularity functions.
Evaluate the deflections at B and C and compare your results with Example 4–10.