Page 187 - Six Sigma for electronics design and manufacturing
P. 187
Six Sigma for Electronics Design and Manufacturing
156
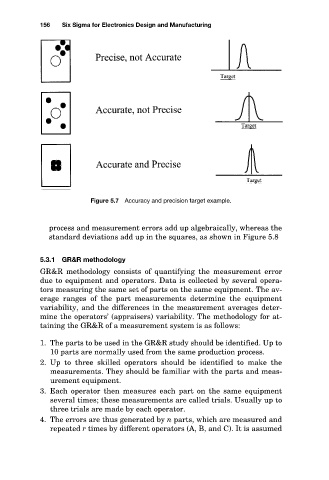
Figure 5.7 Accuracy and precision target example.
process and measurement errors add up algebraically, whereas the
standard deviations add up in the squares, as shown in Figure 5.8
5.3.1 GR&R methodology
GR&R methodology consists of quantifying the measurement error
due to equipment and operators. Data is collected by several opera-
tors measuring the same set of parts on the same equipment. The av-
erage ranges of the part measurements determine the equipment
variability, and the differences in the measurement averages deter-
mine the operators’ (appraisers) variability. The methodology for at-
taining the GR&R of a measurement system is as follows:
1. The parts to be used in the GR&R study should be identified. Up to
10 parts are normally used from the same production process.
2. Up to three skilled operators should be identified to make the
measurements. They should be familiar with the parts and meas-
urement equipment.
3. Each operator then measures each part on the same equipment
several times; these measurements are called trials. Usually up to
three trials are made by each operator.
4. The errors are thus generated by n parts, which are measured and
repeated r times by different operators (A, B, and C). It is assumed