Page 335 -
P. 335
306 PART THREE CONVENTIONAL METHODS FOR SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
Cardinality is the specification of the number of occurrences of one [object] that can be
related to the number of occurrences of another [object]. Cardinality is usually expressed
as simply 'one' or 'many.' For example, a husband can have only one wife (in most cul-
tures), while a parent can have many children. Taking into consideration all combinations
of 'one' and 'many,' two [objects] can be related as
• One-to-one (l:l)—An occurrence of [object] 'A' can relate to one and only one occur-
rence of [object] 'B,' and an occurrence of 'B' can relate to only one occurrence of 'A.'
• One-to-many (l:N)—One occurrence of [object] 'A' can relate to one or many occur-
rences of [object] 'B,' but an occurrence of 'B' can relate to only one occurrence of 'A.'
For example, a mother can have many children, but a child can have only one mother.
• Many-to-many (M:N)—An occurrence of [object] 'A' can relate to one or more occur-
rences of 'B,' while an occurrence of 'B' can relate to one or more occurrences of 'A.'
For example, an uncle can have many nephews, while a nephew can have many uncles.
Cardinality defines “the maximum number of objects that can participate in a rela-
tionship” [TIL93]. It does not, however, provide an indication of whether or not a par-
ticular data object must participate in the relationship. To specify this information,
the data model adds modality to the object/relationship pair.
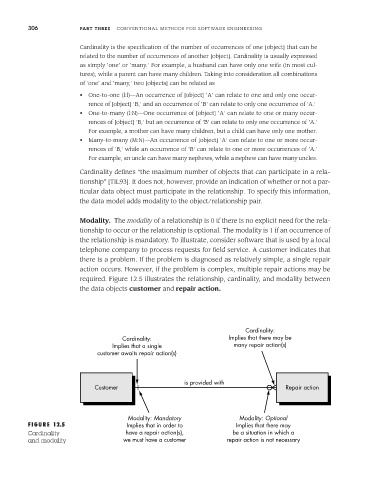
Modality. The modality of a relationship is 0 if there is no explicit need for the rela-
tionship to occur or the relationship is optional. The modality is 1 if an occurrence of
the relationship is mandatory. To illustrate, consider software that is used by a local
telephone company to process requests for field service. A customer indicates that
there is a problem. If the problem is diagnosed as relatively simple, a single repair
action occurs. However, if the problem is complex, multiple repair actions may be
required. Figure 12.5 illustrates the relationship, cardinality, and modality between
the data objects customer and repair action.
Cardinality:
Cardinality: Implies that there may be
Implies that a single many repair action(s)
customer awaits repair action(s)
is provided with
Customer Repair action
Modality: Mandatory Modality: Optional
FIGURE 12.5 Implies that in order to Implies that there may
Cardinality have a repair action(s), be a situation in which a
and modality we must have a customer repair action is not necessary