Page 178 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 178
Dynamics 163
If 0 is a fixed axis or the instantaneous center of zero velocity, then Equation 2-27
reduces to
(2-28)
where I,, is the mass moment of inertia about point 0. I,, may be found from Equation
2-26, or it may be calculated from the parallel axis theorem
I,> = I + ml-' (2-29)
where f is the distance from 0 to the center of mass. The parallel axis theorem may
be used to find I,, regardless of whether I,, is a fixed axis of instantaneous center of
zero velocity.
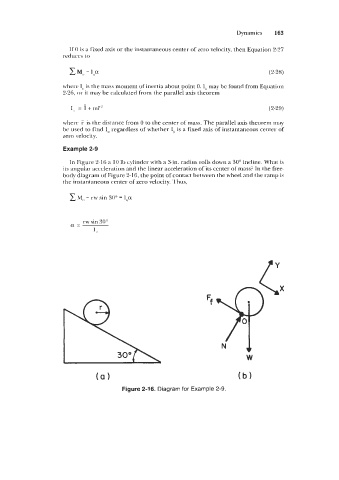
Example 2-9
In Figure 2-16 a 10 lb cylinder with a 3-in. radius rolls down a 30" incline. What is
its angular acceleration and the linear acceleration of its center of mass? In the free-
body diagram of Figure 2-16, the point of contact between the wheel and the ramp is
the instantaneous center of zero velocity. Thus,
Mi, = rw sin 30" = I,,a
a= rw sin 50"
I,,
W
(b)
Figure 2-16. Diagram for Example 2-9.