Page 195 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 195
180 General Engineering and Science
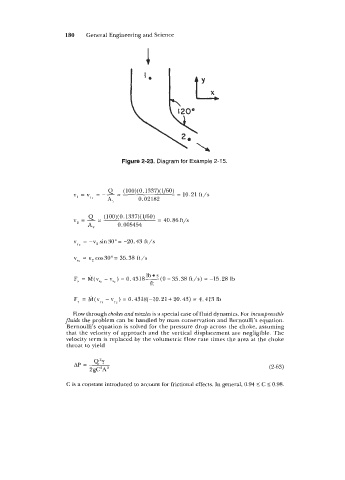
Figure 2-23. Diagram for Example 2-15.
vyp = -v2 sin 30" = -20.43 ft/s
vxp = v2 cos3Oo= 35.38 ft/s
lb s
Fx = M(v,, -vXJ = 0.4318-((0-35.38 ft/s) = -15.28 Ib
ft
FY = M(v,, - vY,) = 0.4318(-10.21+20.43) = 4.413 Ib
Flow through chokes and nozzles is a special case of fluid dynamics. For incompressible
flu& the problem can be handled by mass conservation and Bernoulli's equation.
Bernoulli's equation is solved for the pressure drop across the choke, assuming
that the velocity of approach and the vertical displacement are negligible. The
velocity term is replaced by the volumetric flow rate times the area at the choke
throat to yield
Q'r
AP = ___ (2-63)
2gC2A2
C is a constant introduced to account for frictional effects. In general, 0.94 5 C I 0.98.