Page 239 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 239
212 General Engineering and Science
0 1 W
.L
Q
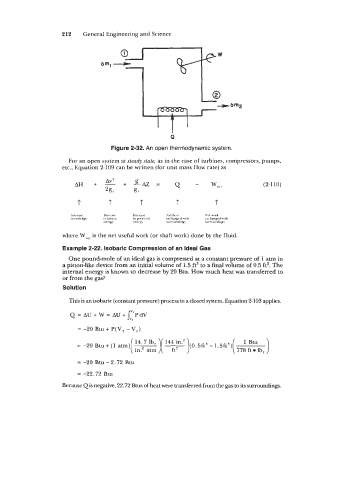
Figure 2-32. An open thermodynamic system.
For an open system at steady state, as in the case of turbines, compressors, pumps,
etc., Equation 2-109 can be written (for unit mass flow rate) as
(2-110)
where W,,, is the net useful work (or shaft work) done by the fluid.
Example 2-22. Isobaric Compression of an Ideal Gas
One pound-mole of an ideal gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 1 atm in
a piston-like device from an initial volume of 1.5 ft3 to a final volume of 0.5 ft3. The
internal energy is known to decrease by 20 Btu. How much heat was transferred to
or from the gas?
Solution
This is an isobaric (constant pressure) process in a closed system. Equation 2-103 applies.
Q = AU + W = AU +j>PdV
I
= -20 Btu + P(V, -VI)
= -20 Btu+(1 atm)
778 ft lb,
= -20 Btu - 2.72 Btu
= -22.72 BtU
Because Qis negative, 22.72 Btus of heat were transferred from the gas to its surroundings.