Page 73 - Sustainability in the Process Industry Integration and Optimization
P. 73
50 Cha p te r F o u r
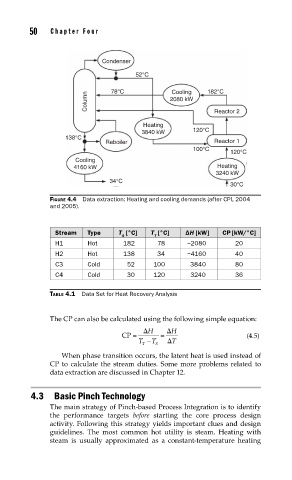
Condenser
52°C
Cooling
Column 78°C 2080 kW 182°C
Reactor 2
Heating
3840 kW 120°C
138°C
Reboiler Reactor 1
100°C
120°C
Cooling
4160 kW Heating
3240 kW
34°C
30°C
FIGURE 4.4 Data extraction: Heating and cooling demands (after CPI, 2004
and 2005).
Stream Type T [°C] T [°C] ΔH [kW] CP [kW/°C]
S T
H1 Hot 182 78 −2080 20
H2 Hot 138 34 −4160 40
C3 Cold 52 100 3840 80
C4 Cold 30 120 3240 36
TABLE 4.1 Data Set for Heat Recovery Analysis
The CP can also be calculated using the following simple equation:
H H
CP (4.5)
T T S T
T
When phase transition occurs, the latent heat is used instead of
CP to calculate the stream duties. Some more problems related to
data extraction are discussed in Chapter 12.
4.3 Basic Pinch Technology
The main strategy of Pinch-based Process Integration is to identify
the performance targets before starting the core process design
activity. Following this strategy yields important clues and design
guidelines. The most common hot utility is steam. Heating with
steam is usually approximated as a constant-temperature heating