Page 109 -
P. 109
76 Part 1 • SyStemS analySiS FundamentalS
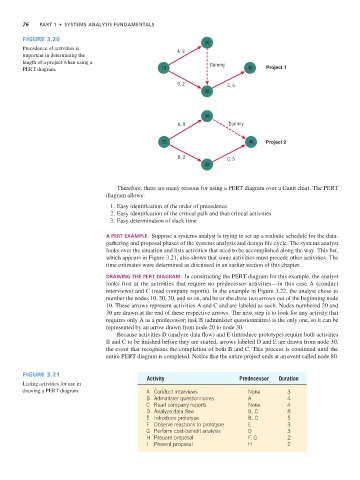
Figure 3.20
20
Precedence of activities is A, 9
important in determining the
length of a project when using a Dummy
PERT diagram. 10 40 Project 1
B,2 C, 5
30
20
A, 9 Dummy
10 40 Project 2
B, 2 C, 5
30
Therefore, there are many reasons for using a PERT diagram over a Gantt chart. The PERT
diagram allows:
1. Easy identification of the order of precedence
2. Easy identification of the critical path and thus critical activities
3. Easy determination of slack time
A PERT EXAMPLE. Suppose a systems analyst is trying to set up a realistic schedule for the data-
gathering and proposal phases of the systems analysis and design life cycle. The systems analyst
looks over the situation and lists activities that need to be accomplished along the way. This list,
which appears in Figure 3.21, also shows that some activities must precede other activities. The
time estimates were determined as discussed in an earlier section of this chapter.
DRAWING THE PERT DIAGRAM. In constructing the PERT diagram for this example, the analyst
looks first at the activities that require no predecessor activities—in this case A (conduct
interviews) and C (read company reports). In the example in Figure 3.22, the analyst chose to
number the nodes 10, 20, 30, and so on, and he or she drew two arrows out of the beginning node
10. These arrows represent activities A and C and are labeled as such. Nodes numbered 20 and
30 are drawn at the end of these respective arrows. The next step is to look for any activity that
requires only A as a predecessor; task B (administer questionnaires) is the only one, so it can be
represented by an arrow drawn from node 20 to node 30.
Because activities D (analyze data flow) and E (introduce prototype) require both activities
B and C to be finished before they are started, arrows labeled D and E are drawn from node 30,
the event that recognizes the completion of both B and C. This process is continued until the
entire PERT diagram is completed. Notice that the entire project ends at an event called node 80.
Figure 3.21
Activity Predecessor Duration
Listing activities for use in
drawing a PERT diagram. A Conduct interviews None 3
B Administer questionnaires A 4
C Read company reports None 4
D Analyze data flow B, C 8
E Introduce prototype B, C 5
F Observe reactions to prototype E 3
G Perform cost-benefit analysis D 3
H Prepare proposal F, G 2
I Present proposal H 2