Page 23 - The Geological Interpretation of Well Logs
P. 23
- THE LOGGING ENVIRONMENT -
distance from borehole
Table 2.2 Depth of investigation of the neutron too)
Go 2 4 6 8
(modified from Serra, 1979, after Schlumberger).
7 > . ‘ 1 100%
- " Porosity Depth* of Investigation
c & i
(%) (cm)
$5
so
Qa 50%
0 60.0
2% | |
5~ 10 34.0
20 23,0
| 30 16.5
0%
*90% of the signal
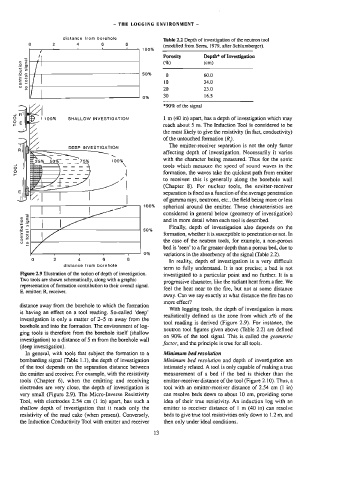
TOOL SHALLOW INVESTIGATION reach about 5 m. The Induction Tool is considered to be
1 m (40 in) apart, has a depth of investigation which may
the most likely to give the resistivity (in fact, conductivity)
of the untouched formation (R)).
The emitter-receiver separation is not the only factor
DEEP INVESTIGATION
~ affecting depth of investigation. Necessarily it varies
TOOL 100% \ with the character being measured. Thus for the sonic
tools which measure the speed of sound waves in the
to receiver: this is generally along the borehole wall
| formation, the waves take the quickest path from emitter
(Chapter 8). For nuclear tools, the emitter-receiver
separation is fixed as a function of the average penetration
of gamma rays, neutrons, etc., the field being more or less
Z 100% spherical around the emitter. These characteristics are
| | “ considered in general below (geometry of investigation)
|e
c s
2s | and in more detail when each tool is described.
the case of the neutron tools, for example, a non-porous
3% Finally, depth of investigation also depends on the
23 50%
22 A formation, whether it is susceptible to penetration or not. In
5 =
oo bed is ‘seen’ to a far greater depth than a porous bed, due to
variations in the absorbency of the signal (Table 2.2).
r
T
0%
T
In reality, depth of investigation is a very difficult
distance from borehole
term to fully understand. It is not precise; a bed is not
Figure 2.9 Hlustration of the notion of depth of investigation.
investigated to a particular point and no further. It is a
Two tools are shown schematically, along with a graphic
progressive character, like the radiant heat from a fire. We
representation of formation contribution to their overall signal.
feel the heat near to the fire, but not at some distance
E, emitter, R, receiver.
away. Can we say exactly at what distance the fire has no
more effect?
distance away from the borehole to which the formation
With logging tools, the depth of investigation is more
is having an effect on a tool reading. So-called ‘deep’
realistically defined as the zone from which x% of the
investigation is only a matter of 2-5 m away from the
tool reading is derived (Figure 2.9). For instance, the
borehole and into the formation. The environment of log-
neutron tool figures given above (Table 2.2) are defined
ging tools is therefore from the borehole itself (shallow
on 90% of the tool signal. This is called the geometric
investigation) to a distance of 5 m from the borehole wal]
factor, and the principle is true for all tools.
(deep investigation).
In general, with tools that subject the formation to a Minimum bed resolution
bombarding signal (Table 1.1), the depth of investigation Minimum bed resolution and depth of investigation are
of the tool depends on the separation distance between intimately related. A tool is only capable of making a true
the emitier and receiver. For example, with the resistivity measurement of a bed if the bed is thicker than the
tools (Chapter 6), when the emitting and receiving emitter-receiver distance of the tool (Figure 2.10). Thus, a
electrodes are very close, the depth of investigation is tool with an emitter-receiver distance of 2.54 cm (1 in)
very small (Figure 2.9). The Micro-Inverse Resistivity can resolve beds down to about 10 cm, providing some
Tool, with electrodes 2.54 cm (1 in) apart, has such a idea of their true resistivity. An induction log with an
shallow depth of investigation that it reads only the emitter to receiver distance of 1 m (40 in) can resolve
resistivity of the mud cake (when present). Conversely, beds to give true tool resistivities only down to 1.2 m, and
the Induction Conductivity Tool with emitter and receiver then only under ideal conditions.
13