Page 60 -
P. 60
System Hydraulics
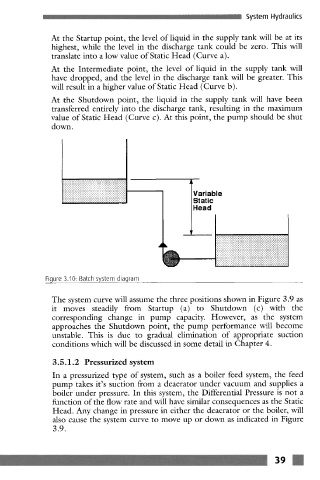
At the Startup point, the level of liquid in the supply tank will be at its
highest, while the level in the discharge tank could be zero. This will
translate into a low value of Static Head (Curve a).
At the Intermediate point, the level of liquid in the supply tank will
have dropped, and the level in the discharge tank will be greater. This
will result in a higher value of Static Head (Curve b).
At the Shutdown point, the liquid in the supply tank will have been
transferred entirely into the discharge tank, resulting in the maximum
value of Static Head (Curve c). At this point, the pump should be shut
down.
iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii i iiiii iiiii iiiii i iii i i !iiiiiiiii!!iiii!
Head
ii••iiiiiii•iii•i•ii•ii•ii•iii•••ii•i•iii•i••iiiii•ii!iiLi•i!iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii•ii•iii
L
:::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
Figure 3.10: Batch system diagram
The system curve will assume the three positions shown in Figure 3.9 as
it moves steadily from Startup (a) to Shutdown (c) with the
corresponding change in pump capacity. However, as the system
approaches the Shutdown point, the pump performance will become
unstable. This is due to gradual elimination of appropriate suction
conditions which will be discussed in some detail in Chapter 4.
3.5.1.2 Pressurized system
In a pressurized type of system, such as a boiler feed system, the feed
pump takes it's suction from a deaerator under vacuum and supplies a
boiler under pressure. In this system, the Differential Pressure is not a
function of the flow rate and will have similar consequences as the Static
Head. Any change in pressure in either the deaerator or the boiler, will
also cause the system curve to move up or down as indicated in Figure
3.9.
39