Page 36 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 36
-
Porous metal bearings A6
DESIGN AND MATERIAL SELECTION
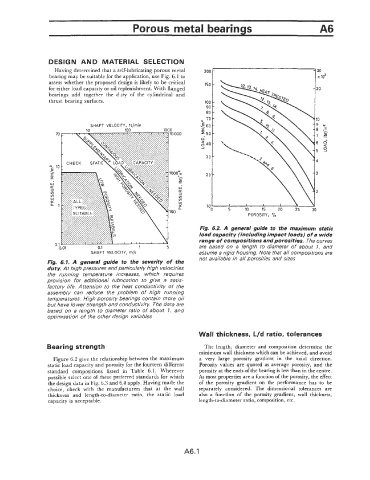
Having determined that a self-lubricating porous metal
bearing may be suitable for the application, use Fig. 6.1 to
assess whether the proposed design is likely to be critical 150 -
for either load capacity or oil replenishment. With flanged
bearings add together the duty of the cylindrical and
thrust bearing surfaces. 100 -
90 -
-
80
N 'O-
SHAFT VELOCITY, ft/rnin <60 -
2
50 -
0-
40-
-
30
-
20
2
20
30
25
15
10
'OO 5
POROSITY, '10
Fig. 6.2. A general guide to the maximum static
load capacity (including impact loads) of a wide
range of compositions and porosities. The curves
are based on a length to diameter of about 1. and
SHAFT VELOCITY, rn/s assume a rigid housing. Note that all compositions are
not available in all porosities and sizes
1. A general guide to the severity of the
duty. At high pressures and particularly high velocities
the running temperature increases, which requires
provision for additional lubrication to give a satis-
factory life. Attention to the heat conductivity of the
assembly can reduce the problem of high running
temperatures. High porosity bearings contain more oil
but have lower strength and conductivity. The data are
based on a length fo diameter ratio of about 1. and
optimisation of rhe other design variables
Wall thickness, L/d ratio, tolerances
Bearing strength The length, diameter and composition determine the
minimum wall thickness which can be achieved, and avoid
Figure 6.2 give the relationship between the maximum a very large porosity gradient in the axial direction.
static load capacity and porosity for the fourteen different Porosity values are quoted as average porosity, and the
standard compositions listed in Table 6.1. Wherever porosity at the ends of the bearing is less than in the centre.
possible select one of these preferred standards for which As most properties are a function of the porosity, the effect
the design data in Fig. 6.3 and 6.4 apply. Having made the of the porosity gradient on the performance has to be
choice, check with the manufacturers that at the wall separately considered. The dimensional tolerances are
thickness and length-to-diameter ratio, the static load also a function of the porosity gradient, wall thickness,
capacity is acceptable. length-to-diameter ratio, composition, etc.
A6.1