Page 1135 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1135
allows units to use different clocks, but the lack of a shared clock makes it necessary to use extra signals
to determine the validity of bus signals.
42.4 Instruction Set Architecture
There are several elements that characterize an instruction set architecture, including word size, instruc-
tion encoding, and architecture model.
Word Size
Programs often differ in the size of data they prefer to manipulate. Word processing programs operate
on 8-bit or 16-bit data that correspond to characters in text documents. Many applications require 32-bit
integer data to avoid frequent overflow in arithmetic calculation. Scientific computation often requires
64-bit floating-point data to achieve desired accuracy. Operating systems and databases may require
64-bit integer data to represent a very large name space with integers. As a result, the processors are
usually designed to access multiple-byte data from memory systems. This is a well-known source of
complexity in microprocessor design.
The endian convention specifies the numbering of bytes with a memory word. In the little endian
convention, the least significant byte in a word is numbered byte 0. The number increases as the positions
increase in significance. The DEC VAX and X86 architectures follow the little endian convention. In the
big endian convention, the most significant byte in a word is numbered 0. The number decreases as the
positions decrease in significance. The IBM 360/370, HP PA-RISC, Sun SPARC, and Motorola 680X0
architectures follow the big endian convention. The difference usually manifests itself when users try to
transfer binary files between machines using different endian conventions.
Instruction Encoding
Instruction encoding plays an important role in the code density and performance of microprocessors.
Traditionally, the cost of memory capacity was the determining factor in designing either a fixed-length
or variable-length instruction set. Fixed-length instruction encoding assigns the same encoding size to
all instructions. Fixed-length encoding is generally a characteristic of modern microprocessors and the
product of the increasing advancements in memory capacity.
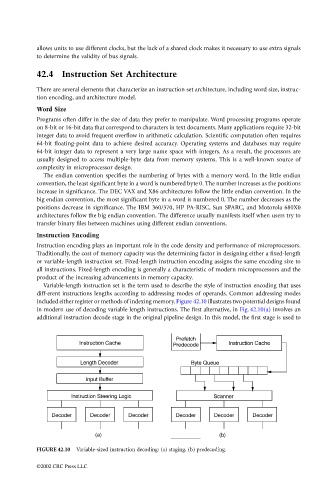
Variable-length instruction set is the term used to describe the style of instruction encoding that uses
diff-erent instructions lengths according to addressing modes of operands. Common addressing modes
included either register or methods of indexing memory. Figure 42.10 illustrates two potential designs found
in modern use of decoding variable length instructions. The first alternative, in Fig. 42.10(a) involves an
additional instruction decode stage in the original pipeline design. In this model, the first stage is used to
FIGURE 42.10 Variable-sized instruction decoding: (a) staging, (b) predecoding.
©2002 CRC Press LLC