Page 731 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 731
0066_Frame_C23 Page 39 Wednesday, January 9, 2002 1:55 PM
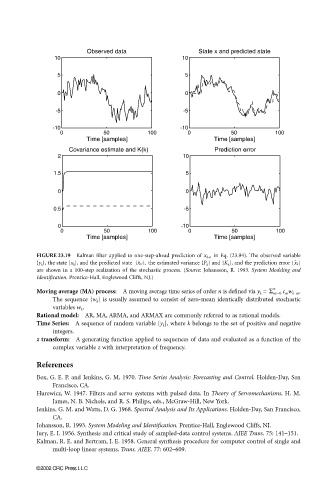
Observed data State x and predicted state
10 10
5 5
0 0
-5 -5
-10 -10
0 50 100 0 50 100
Time [samples] Time [samples]
Covariance estimate and K(k) Prediction error
2 10
1.5 5
0 0
0.5 -5
0 -10
0 50 100 0 50 100
Time [samples] Time [samples]
FIGURE 23.19 Kalman filter applied to one-step-ahead prediction of x k+1 in Eq. (23.94). The observed variable
{y k }, the state {x k }, and the predicted state {x ˆ k}, the estimated variance {P k } and {K k }, and the prediction error {x ˜ }
k
are shown in a 100-step realization of the stochastic process. (Source: Johansson, R. 1993. System Modeling and
Identification. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.)
n
Moving average (MA) process: A moving average time series of order n is defined via y k = Σ m=0 c m w k−m .
The sequence {w k } is usually assumed to consist of zero-mean identically distributed stochastic
variables w k .
Rational model: AR, MA, ARMA, and ARMAX are commonly referred to as rational models.
Time Series: A sequence of random variable {y k }, where k belongs to the set of positive and negative
integers.
z transform: A generating function applied to sequences of data and evaluated as a function of the
complex variable z with interpretation of frequency.
References
Box, G. E. P. and Jenkins, G. M. 1970. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. Holden-Day, San
Francisco, CA.
Hurewicz, W. 1947. Filters and servo systems with pulsed data. In Theory of Servomechanisms, H. M.
James, N. B. Nichols, and R. S. Philips, eds., McGraw-Hill, New York.
Jenkins, G. M. and Watts, D. G. 1968. Spectral Analysis and Its Applications. Holden-Day, San Francisco,
CA.
Johansson, R. 1993. System Modeling and Identification. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Jury, E. I. 1956. Synthesis and critical study of sampled-data control systems. AIEE Trans. 75: 141–151.
Kalman, R. E. and Bertram, J. E. 1958. General synthesis procedure for computer control of single and
multi-loop linear systems. Trans. AIEE. 77: 602–609.
©2002 CRC Press LLC