Page 16 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 16
1.3 Binding of Hydrogen Ions and Magnesium Ions by Adenosine Triphosphate 9
The acid dissociation constants can be calculated from In P by fitting the plot of
P versus [H'] with a power series in [H'].
ATP also binds magnesium ions as shown by the three complex ion
dissociation constants in Table 1.2. Incorporating these species into equations
1.3-1 and 1.3-2 yields the following binding polynomial for ATP:
CH+I2 +- CMg2+l + CMg2+ICH+I + CME2+I2
P=l+- CH+I +
KIATPK2ATP K3ATP KlATPK4ATP K3ATPK5ATP
(1.3- 12)
Now the binding of hydrogen ions is given by the following partial derivatives of
the binding polynomial:
- [H'] ( dP )
__
N,=- -- -1 (i31nP)pMg =[H'] (ainP)
-
~
P d[H+] pMg ln(10) apH pMg
(1.3-13)
The average binding of magnesium ions NH is given by the following partial
derivatives of the binding polynomial:
( 1.3- 14)
These differentiations yield
+ CMg2+ICH+I
- KlATPK2ATP KlATPK4ATP
N, =
1 +-
( 1.3- 15)
(1.3- 16)
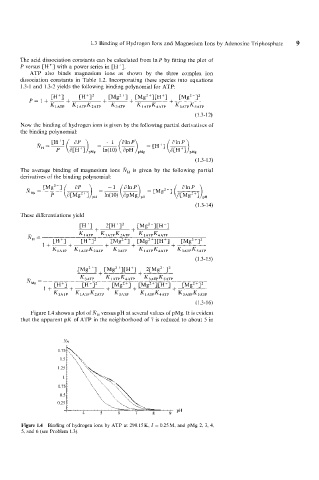
Figure 1.4 shows a plot of NH versus pH at several values of pMg. It is evident
that the apparent pK of ATP in the neighborhood of 7 is reduced to about 5 in
Figure 1.4 Binding of hydrogen ions by ATP at 298.15 K, I = 0.25 M, and pMg 2, 3, 4,
5, and 6 (see Problem 1.3).