Page 704 - Bird R.B. Transport phenomena
P. 704
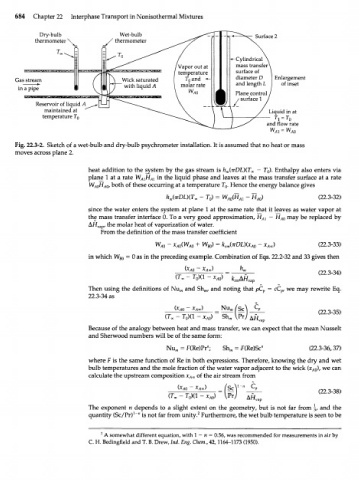
684 Chapter 22 Interphase Transport in Nonisothermal Mixtures
Dry-bulb Wet-bulb Surface 2
thermometer thermometer
-*- Cylindrical
Vapor out at mass transfer
temperature surface of
Gas stream Wick saturated T and •*- diameter D Enlargement
o
• — • with liquid A molar rate and length L of inset
in a pipe W Plane control
surface 1
Reservoir of liquid A
maintained at Liquid in at
temperature T h
o 0
and flow rate
Fig. 22.3-2. Sketch of a wet-bulb and dry-bulb psychrometer installation. It is assumed that no heat or mass
moves across plane 2.
heat addition to the system by the gas stream is h (7rDL)(T K - T ). Enthalpy also enters via
o
m
plane 1 at a rate W H Al in the liquid phase and leaves at the mass transfer surface at a rate
M
W H , both of these occurring at a temperature T . Hence the energy balance gives
AO
A0
o
- To) = - H ) (22.3-32)
A0
since the water enters the system at plane 1 at the same rate that it leaves as water vapor at
the mass transfer interface 0. To a very good approximation, H A] - H AQ may be replaced by
AH , the molar heat of vaporization of water.
vap
From the definition of the mass transfer coefficient
O + W ) = k (7rDD(x A0 - x J (22.3-33)
xm
B0
A
in which W B0 = 0 as in the preceding example. Combination of Eqs. 22.2-32 and 33 gives then
(22.3-34)
- T )(l -
0
Then using the definitions of Nu w and Sh , and noting that pC p = cC , we may rewrite Eq.
p
m
22.3-34 as
(22.3-35)
(T. - T )(l - x ) Sh \?r
0 A0 m -*vap
Because of the analogy between heat and mass transfer, we can expect that the mean Nusselt
and Sherwood numbers will be of the same form:
Nu = HRe)Pr"; Sh = F(Re)Sc" (22.3-36,37)
M m
where F is the same function of Re in both expressions. Therefore, knowing the dry and wet
bulb temperatures and the mole fraction of the water vapor adjacent to the wick (х ), we can
ло
calculate the upstream composition x Aoo of the air stream from
х ) Sc (22.3-38)
Аж
(Т. - То)<1 - x ) AH, vap
A0
The exponent n depends to a slight extent on the geometry, but is not far from |, and the
1
2
quantity (Sc/Pr) "" is not far from unity. Furthermore, the wet bulb temperature is seen to be
2 A somewhat different equation, with 1 - n = 0.56, was recommended for measurements in air by
С. Н. Bedingfield and Т. В. Drew, Ind. Eng. Chem., 42,1164-1173 (1950).