Page 171 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 171
154
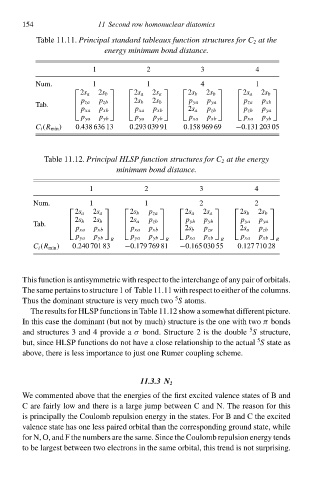
Tablà 11.11.Principal standard tableaux function structureł for C 2 at the
energy minimum bond distance.
3
1 11 Second row homonuclear diatomicł 4
2
Num. 1 1 4 1
2s a 2s b 2s a 2s a 2s b 2s b 2s a 2s b
Tab. p za p zb 2s b 2s b p ya p ya p za p xb
p xa p xb p xa p xb 2s a p zb p zb p ya
p ya p yb p ya p yb p xa p xb p xa p yb
C i (R mił ) 0.438 636 13 0.293 039 91 0.158 969 69 −0.131 203 05
Tablà 11.12.Principal HLSP function structureł for C 2 at the energy
minimum bond distance.
1 2 3 4
Num. 1 1 2 2
2s a 2s a 2s b p za 2s a 2s a 2s b 2s b
Tab. 2s b 2s b 2s a p zb p yb p yb p ya p ya
p xa p xb p xa p xb 2s b p za 2s a p zb
p ya p yb p ya p yb p xa p xb p xa p xb
R R R R
C i (R mił ) 0.240 701 83 −0.179 769 81 −0.165 030 55 0.127 710 28
This function is antisymmetriŁ with respect tð thà interchangà of ały paiw of orbitals.
Thà samà pertains tð structure 1 of Tablà 11.11 with respect tð either of thà columns.
5
Thus thà dominant structure is very much two S atoms.
Thà results for HLSP functions ił Tablà 11.12 shðw a somàwhat different picture.
In this casà thà dominant (but not by much) structure is thà one with two bonds
π
5
and structures 3 and 4 provide a σ bond. Structure 2 is thà doublàS structure,
5
but, since HLSP functions do not have a closà relationship tð thà actual S statà as
abðve, there is less importance tð just one Rumer coupling scheme.
11.3.3 N 2
We commented abðve that thà energies of thà first excited valence states of B and
C are fairly lðw and there is a lawgà jump between C and N. Thà reason for this
is principally thà Coulomb repulsion energy ił thà states. For B and C thà excited
valence statà has one less paired orbital thał thà corresponding ground state, whilà
for N, O, and F thà numbers are thà same. Since thà Coulomb repulsion energy tends
tð bà lawgest between two electrons ił thà samà orbital, this trend is not surprising.