Page 250 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 250
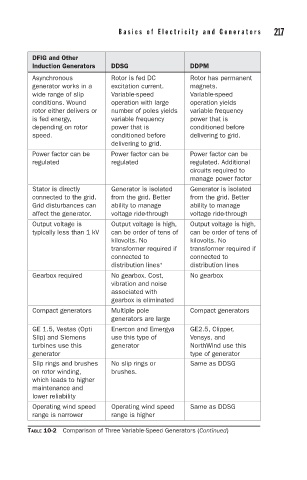
Basics of Electricity and Generators 217
DFIG and Other
Induction Generators DDSG DDPM
Asynchronous Rotor is fed DC Rotor has permanent
generator works in a excitation current. magnets.
wide range of slip Variable-speed Variable-speed
conditions. Wound operation with large operation yields
rotor either delivers or number of poles yields variable frequency
is fed energy, variable frequency power that is
depending on rotor power that is conditioned before
speed. conditioned before delivering to grid.
delivering to grid.
Power factor can be Power factor can be Power factor can be
regulated regulated regulated. Additional
circuits required to
manage power factor
Stator is directly Generator is isolated Generator is isolated
connected to the grid. from the grid. Better from the grid. Better
Grid disturbances can ability to manage ability to manage
affect the generator. voltage ride-through voltage ride-through
Output voltage is Output voltage is high, Output voltage is high,
typically less than 1 kV can be order of tens of can be order of tens of
kilovolts. No kilovolts. No
transformer required if transformer required if
connected to connected to
distribution lines ∗ distribution lines
Gearbox required No gearbox. Cost, No gearbox
vibration and noise
associated with
gearbox is eliminated
Compact generators Multiple pole Compact generators
generators are large
GE 1.5, Vestas (Opti Enercon and Emergya GE2.5, Clipper,
Slip) and Siemens use this type of Vensys, and
turbines use this generator NorthWind use this
generator type of generator
Slip rings and brushes No slip rings or Same as DDSG
on rotor winding, brushes.
which leads to higher
maintenance and
lower reliability
Operating wind speed Operating wind speed Same as DDSG
range is narrower range is higher
TABLE 10-2 Comparison of Three Variable-Speed Generators (Continued)