Page 248 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 248
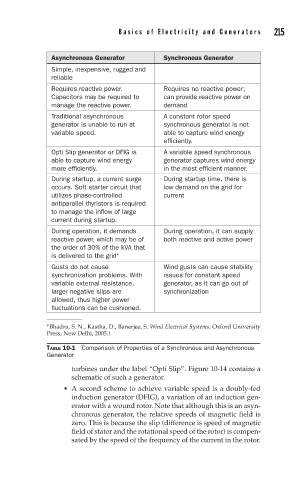
Basics of Electricity and Generators 215
Asynchronous Generator Synchronous Generator
Simple, inexpensive, rugged and
reliable
Requires reactive power. Requires no reactive power;
Capacitors may be required to can provide reactive power on
manage the reactive power. demand
Traditional asynchronous A constant rotor speed
generator is unable to run at synchronous generator is not
variable speed. able to capture wind energy
efficiently.
Opti Slip generator or DFIG is A variable speed synchronous
able to capture wind energy generator captures wind energy
more efficiently. in the most efficient manner.
During startup, a current surge During startup time, there is
occurs. Soft starter circuit that low demand on the grid for
utilizes phase-controlled current
antiparallel thyristors is required
to manage the inflow of large
current during startup.
During operation, it demands During operation, it can supply
reactive power, which may be of both reactive and active power
the order of 30% of the kVA that
is delivered to the grid ∗
Gusts do not cause Wind gusts can cause stability
synchronization problems. With issues for constant speed
variable external resistance, generator, as it can go out of
larger negative slips are synchronization
allowed, thus higher power
fluctuations can be cushioned.
Bhadra, S. N., Kastha, D., Banerjee, S. Wind Electrical Systems, Oxford University
∗
Press, New Delhi, 2005.)
TABLE 10-1 Comparison of Properties of a Synchronous and Asynchronous
Generator
turbines under the label “Opti Slip”. Figure 10-14 contains a
schematic of such a generator.
A second scheme to achieve variable speed is a doubly-fed
induction generator (DFIG), a variation of an induction gen-
erator with a wound rotor. Note that although this is an asyn-
chronous generator, the relative speeds of magnetic field is
zero. This is because the slip (difference is speed of magnetic
field of stator and the rotational speed of the rotor) is compen-
sated by the speed of the frequency of the current in the rotor.