Page 253 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 253
STATIONARY BLADE LOADING 227
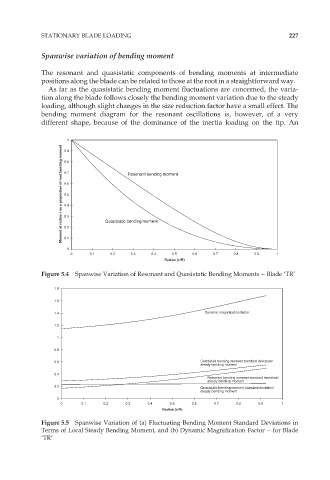
Spanwise variation of bending moment
The resonant and quasistatic components of bending moments at intermediate
positions along the blade can be related to those at the root in a straightforward way.
As far as the quasistatic bending moment fluctuations are concerned, the varia-
tion along the blade follows closely the bending moment variation due to the steady
loading, although slight changes in the size reduction factor have a small effect. The
bending moment diagram for the resonant oscillations is, however, of a very
different shape, because of the dominance of the inertia loading on the tip. An
1
Moment at radius r as a proportion of root bending moment 0.7 Quasistatic bending moment
0.9
0.8
Resonant bending moment
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
Radius (r/R)
Figure 5.4 Spanwise Variation of Resonant and Quasistatic Bending Moments – Blade ‘TR’
1.8
1.6
1.4 Dynamic magnification factor
1.2
1
0.8
0.6 Combined bending moment standard deviation/
steady bending moment
0.4
Resonant bending moment standard deviation/
steady bending moment
0.2 Quasistatic bending moment standard deviation/
steady bending moment
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
Radius (r/R)
Figure 5.5 Spanwise Variation of (a) Fluctuating Bending Moment Standard Deviations in
Terms of Local Steady Bending Moment, and (b) Dynamic Magnification Factor – for Blade
‘TR’