Page 468 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 468
442 COMPONENT DESIGN
Stator
circuit
Local Wound rotor
transformer Rotor induction
circuit machine
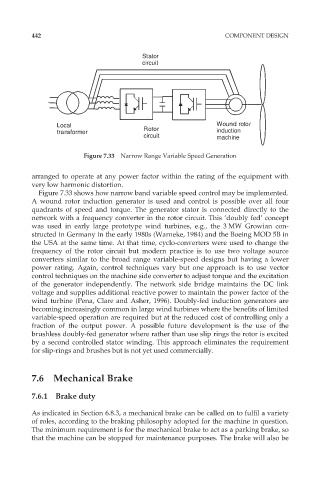
Figure 7.33 Narrow Range Variable Speed Generation
arranged to operate at any power factor within the rating of the equipment with
very low harmonic distortion.
Figure 7.33 shows how narrow band variable speed control may be implemented.
A wound rotor induction generator is used and control is possible over all four
quadrants of speed and torque. The generator stator is connected directly to the
network with a frequency converter in the rotor circuit. This ‘doubly fed’ concept
was used in early large prototype wind turbines, e.g., the 3 MW Growian con-
structed in Germany in the early 1980s (Warneke, 1984) and the Boeing MOD 5B in
the USA at the same time. At that time, cyclo-converters were used to change the
frequency of the rotor circuit but modern practice is to use two voltage source
converters similar to the broad range variable-speed designs but having a lower
power rating. Again, control techniques vary but one approach is to use vector
control techniques on the machine side converter to adjust torque and the excitation
of the generator independently. The network side bridge maintains the DC link
voltage and supplies additional reactive power to maintain the power factor of the
wind turbine (Pena, Clare and Asher, 1996). Doubly-fed induction generators are
becoming increasingly common in large wind turbines where the benefits of limited
variable-speed operation are required but at the reduced cost of controlling only a
fraction of the output power. A possible future development is the use of the
brushless doubly-fed generator where rather than use slip rings the rotor is excited
by a second controlled stator winding. This approach eliminates the requirement
for slip-rings and brushes but is not yet used commercially.
7.6 Mechanical Brake
7.6.1 Brake duty
As indicated in Section 6.8.3, a mechanical brake can be called on to fulfil a variety
of roles, according to the braking philosophy adopted for the machine in question.
The minimum requirement is for the mechanical brake to act as a parking brake, so
that the machine can be stopped for maintenance purposes. The brake will also be